- Flea and Lice Bites
- Lice
- Fleas and lice
- Fleas
In order for the fight against bloodsuckers to be effective, you need to know the differences between fleas and lice, because you need to destroy them in different ways. To see the difference, you need to carefully look at the appearance, study the method of reproduction and nutrition of both types of insects.
Whom the parasites bite
Fleas and lice in humans, blood is used as a food source. But if the former is practically indifferent to whom to bite and whose blood to consume, the latter is quite scrupulous in this matter: she prefers to eat only a specific “host”. So, a human louse will not settle on a rabbit, whereas cat flea “Without any embarrassment” can attack people.
Fleas are “more pleasant” to drink the blood of a permanent owner, but if he is not nearby, he will easily dine with any warm-blooded animals. It is necessary to choose the right remedy for lice and fleas in order to forget about dangerous bloodsuckers as soon as possible.
Important!
Even one female of any species, surviving after processing, is able to breed an insect colony.
Parasite harm
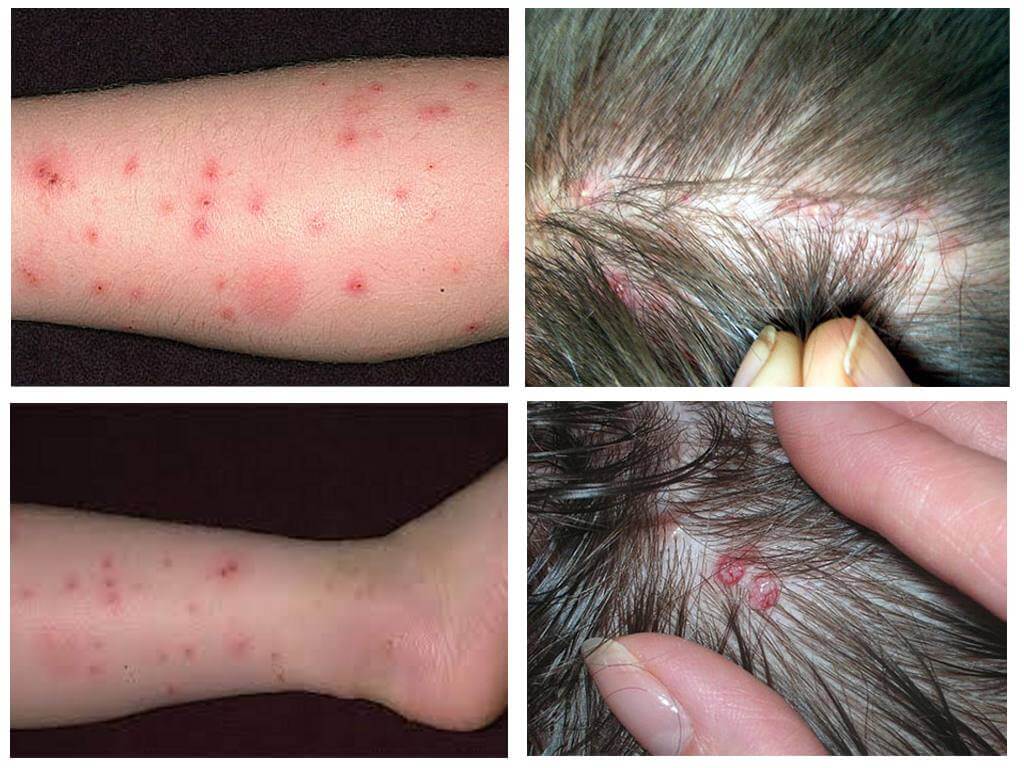
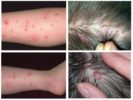
Both types of main damage is done through bites. Insect saliva enters the wound, causing itching. Combing places of bites, a person more and more injures the skin, often brings an infection. There are frequent cases of an allergic reaction to the bloodsucker saliva. For most people, the aesthetic component is also important - bitten skin looks completely unattractive.
Since the difference between fleas and lice is less constancy, it is easy to assume that getting a diverse infection from fleas is much higher. Omnivore makes flea more parasite dangerous to people. Particularly terrible for humans are insects that prefer rats - they can spread typhoid and plague. In addition to serious diseases, helminths are tolerated. One type of louse settles on a person, dividing into subspecies. They are able to carry various types of typhoid.
Lifestyle Differences
Knowing how to distinguish fleas from lice by their lifestyle, you can quickly get rid of bloodsuckers in the house.
So, the louse constantly lives in the hairline of the owner, holding on to the hairs. Ideally, she never leaves her “pasture”.
The difference between fleas and lice, from their lifestyle is that they are not tied to the warm-blooded, freely migrate around the apartment or yard, looking for new sources of food.
Interesting!
To answer who jumps lice or fleas, just look at the structure of both individuals. The legs of insects living in human hair are generally not suitable for jumping, they only run relatively quickly. Whereas fleas can jump so that they cover a distance exceeding its size a hundred times.
Appearance
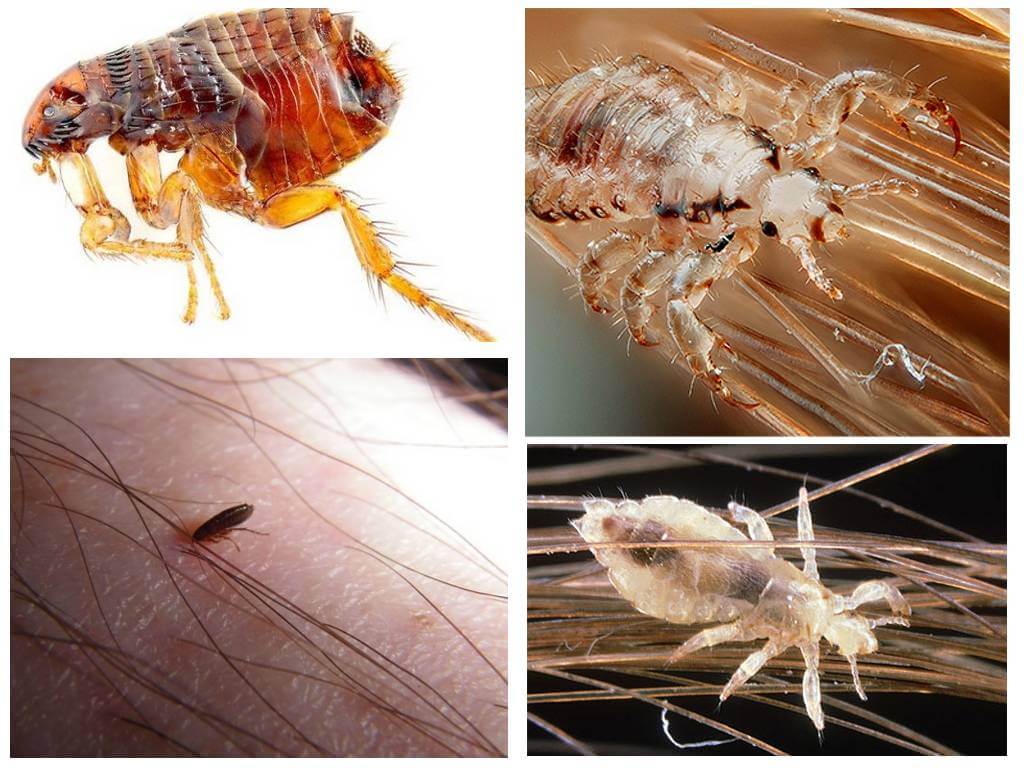

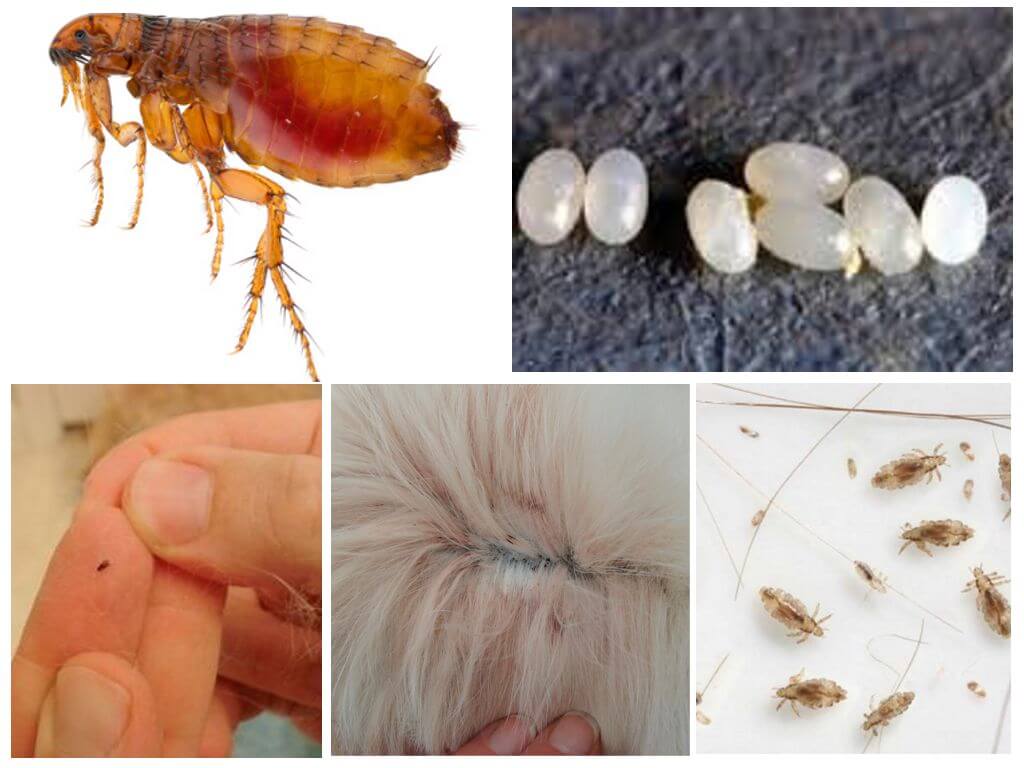
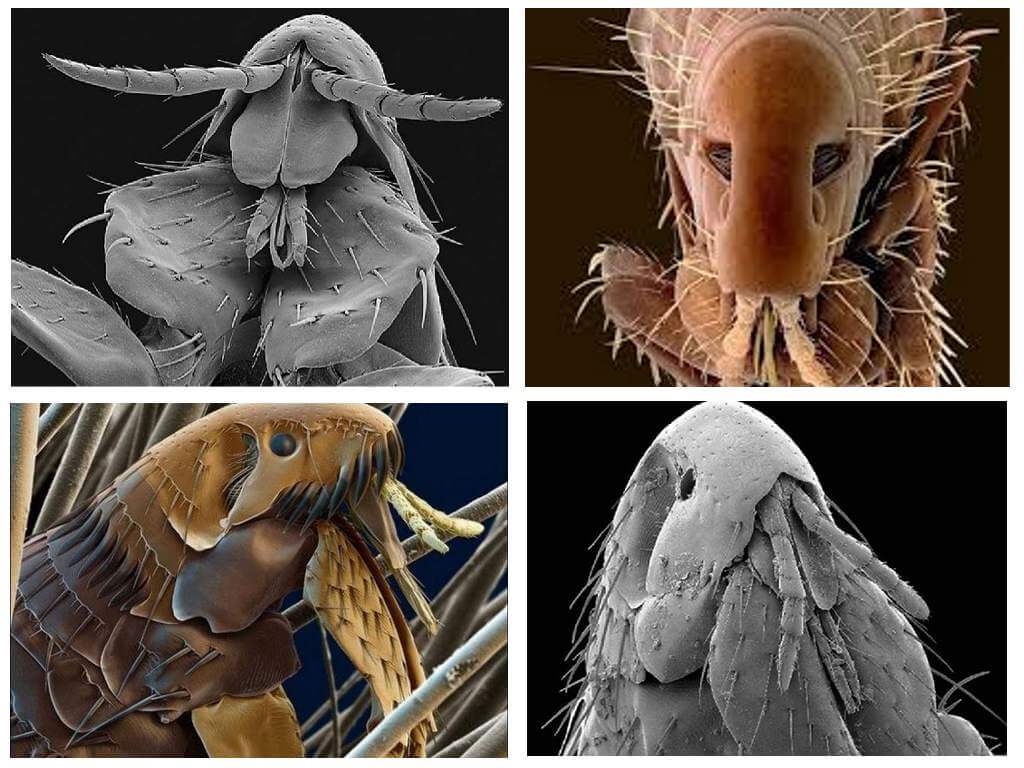
Particularly clearly visible differences in the photo. Both types of parasites should be considered in order to be able to immediately recognize them. Fleas and lice in the photo are clearly visible, as is each difference between them:
- The body of the flea is flattened on its sides, while the louse has a flat body.
- Lice differ from fleas in size - the first ones are smaller.
- Fleas are brown in color: from light to dark. Whereas human parasites are translucent or grayish. When filled with blood, they turn dark red or black.
- The paws of the "jumpers" are long, the third - race - the pair of legs stands out especially.The insects parasitizing on the human head have short paws with hooks at the ends with which they hold on to the hairs.
Breeding
Flea differs from lice not only in appearance, but also reproduction mechanism. This information can help in the fight against bloodsuckers.
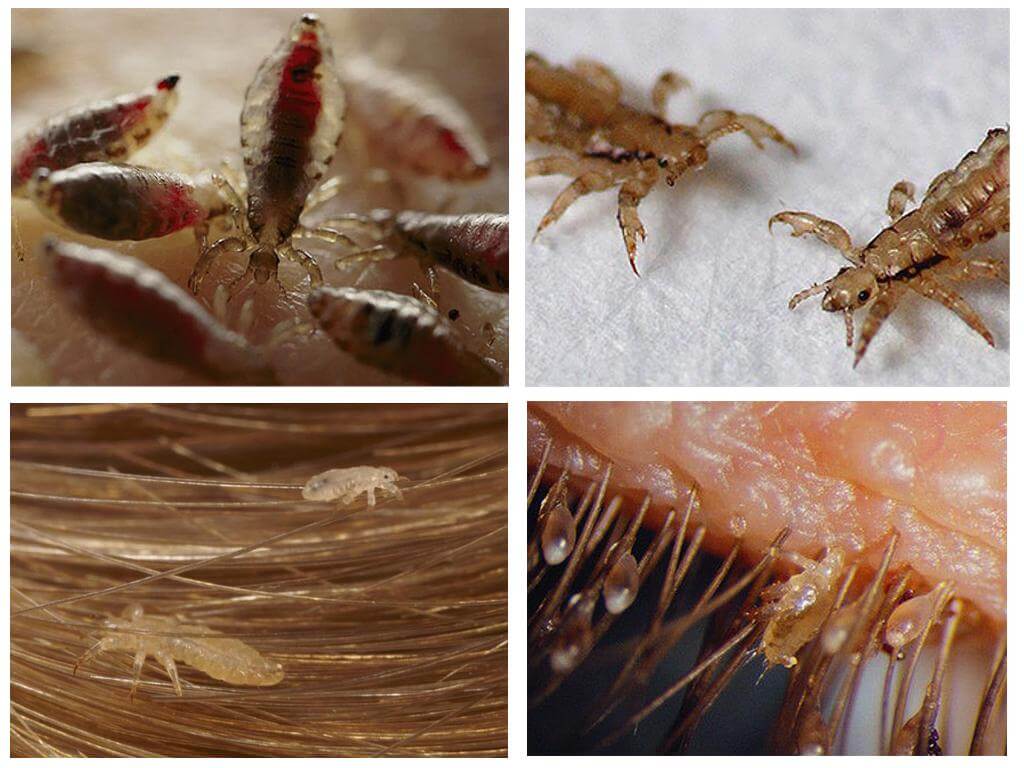
Lice
Continuing to describe the differences between lice and fleas, it should be said that the former practically do not leave their homes, only in exceptional cases, running onto the head of another person in close contact. For one and a half to two months of life, lice lay only 150 eggs, called nits. Light eggs of lice can differ well in dark hair. An adult insect leaves them after about 7 days.

Interesting!
In the female's body, special substances are produced, thanks to which, insects reliably attach their offspring to the hair. This substance is so sticky that even tearing off nits with nails can be difficult.
Fleas
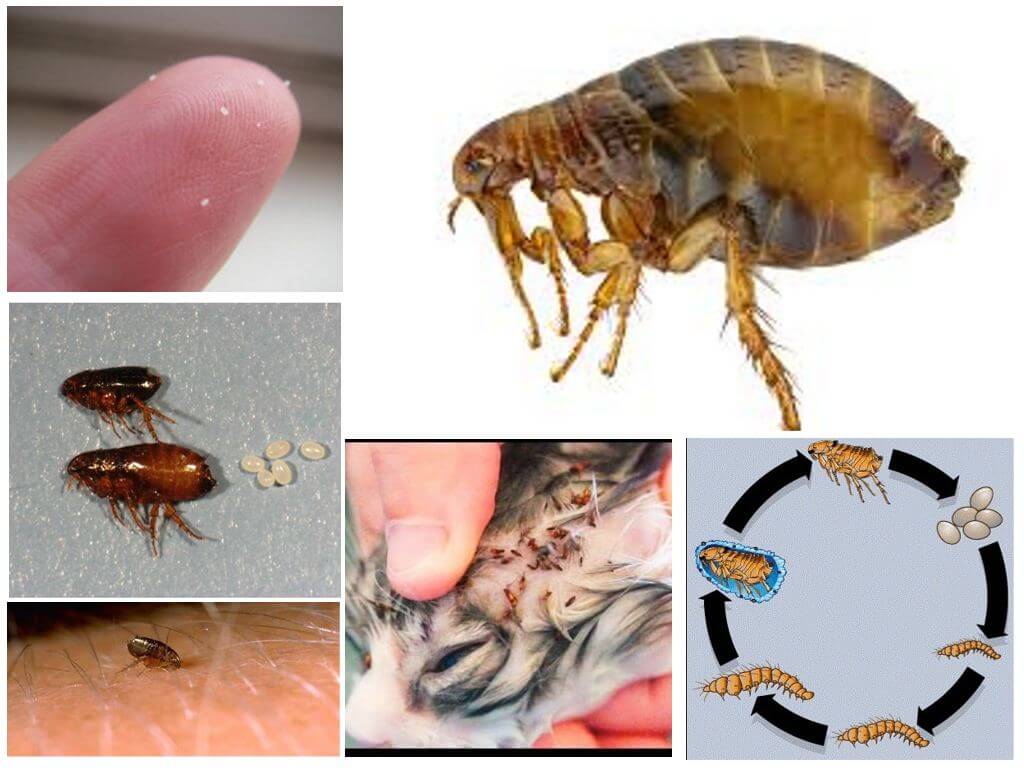
These "jumpers" almost never lay their eggs on the "breadwinner", preferring nooks and crannies. That is why they need to be destroyed outside of animals. Flea eggs can mature from two weeks to several months. After that, a larva emerges from them, preferring other types of food than adults.
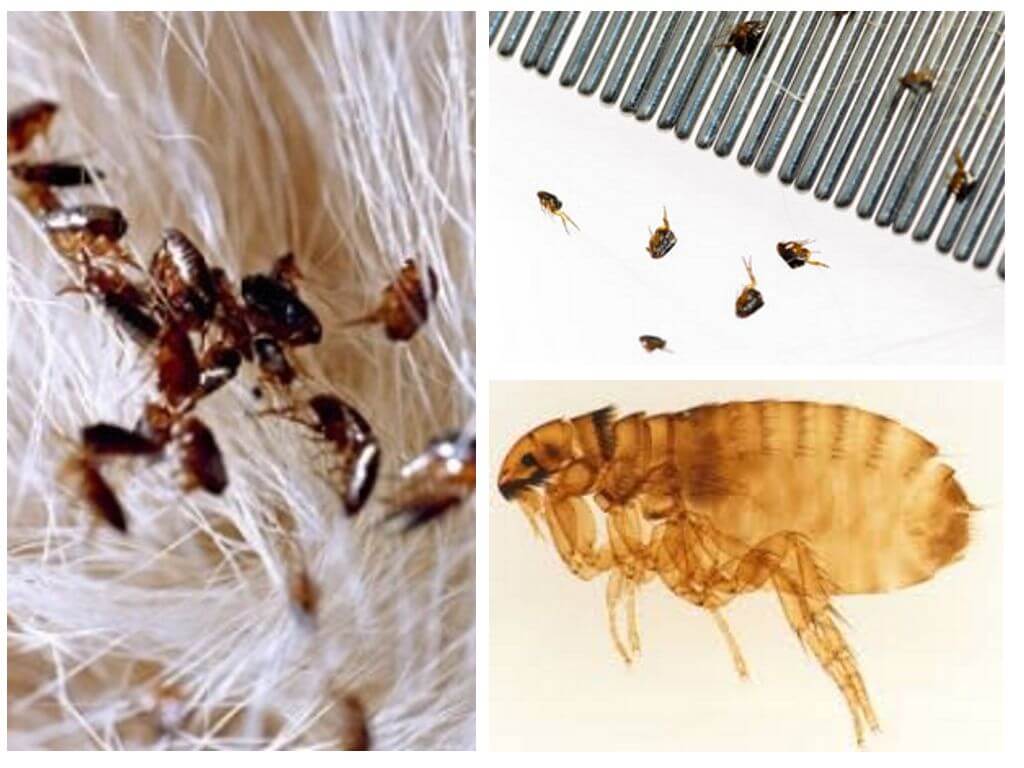

The offspring of lice are nits, and fleas - eggs can be distinguished among themselves according to the places of localization and stickiness of the membrane. Nits are always located in the hairline and when there are too many, it seems that the hair is thickly covered with dandruff. Flea eggs can be found anywhere in the apartment: on the floor, on upholstered and cabinet furniture.
Parasite control
So, it becomes clear that not only do fleas and lice look different, but they also behave differently. Means of dealing with them should be chosen at different points of sale.
Their fleas and nits are difficult to destroy. The fight should include several stages:
- extermination of insects on animals;
- apartment processing;
- processing of common areas.
To destroy fleas from pets, it is recommended to purchase special tools:
- Shampoos for dogs and cats.
- Drops. Such drugs have proven themselves well: Barrier, Dana Ultra Neo, Blokhnet, Celandine.
- Anti-flea collars for dogs and for cats.
To process the premises in a house or apartment, insecticidal preparations such as:
To defeat pediculosis, you need to purchase special funds at the pharmacy. Treatment should consist of two stages:
- the destruction of adult insects;
- getting rid of nits.
Eggs will have to be manually removed or a comb with frequent teeth should be used.
It is very important to boil and carefully wash the laundry, clothes, bedding.
Having determined lice or fleas in a person, you can get rid of them quickly enough by using suitable means of control.