- Giant japanese hornet
- Giant japanese hornet
Almost every person in his life had to experience bee or wasp sting. Contact with a stinging insect is very sensitive, usually accompanied by pain and itching. However, the Japanese hornet poses a much greater danger, the bite of which can be fatal. According to statistics, every year in Japan, over 4 dozen people die from the bites of such giants. Moreover, referring to the reviews of people who suffered from such creatures, they did not experience more painful bites in their life. It is also surprising that an insect is capable of even stinging an enemy, approaching danger, whose dimensions are many times greater than its own.
Insect features
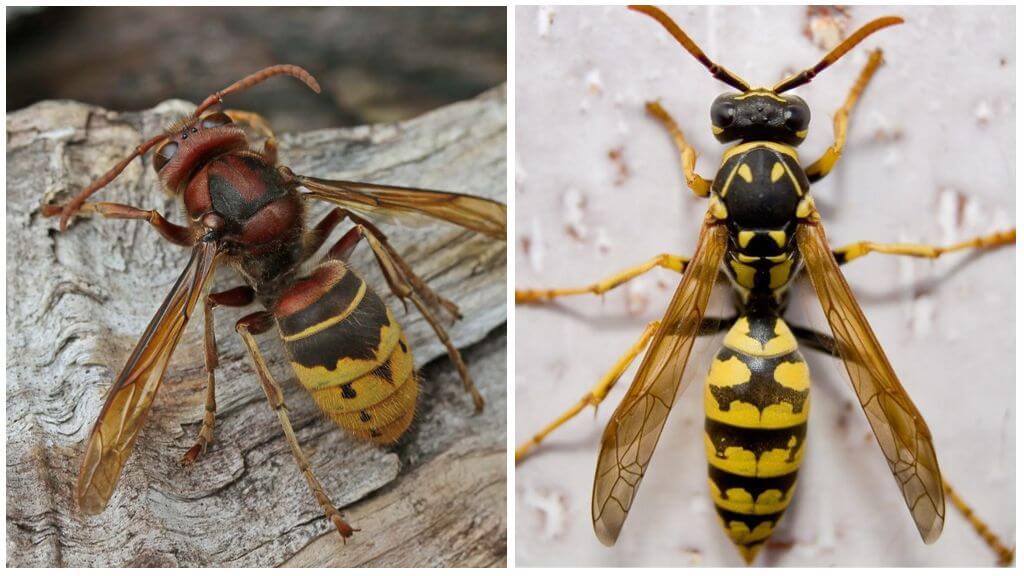
The huge Japanese hornet, referred to as the "sparrow bee", does not at all resemble a friendly bird. Moreover, the stinging insect has a very aggressive character.
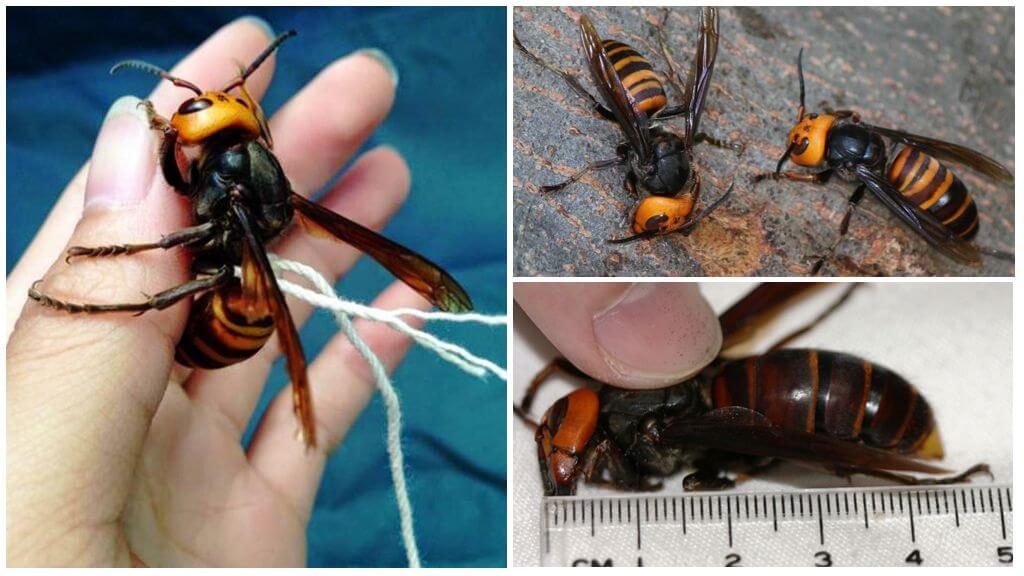
Vespa mandarinia japonica (giant Japanese hornet) differs from its counterparts not only in color, but also in large size:
- It is an insect up to 5 cm, the wingspan of which reaches 6-7 cm.
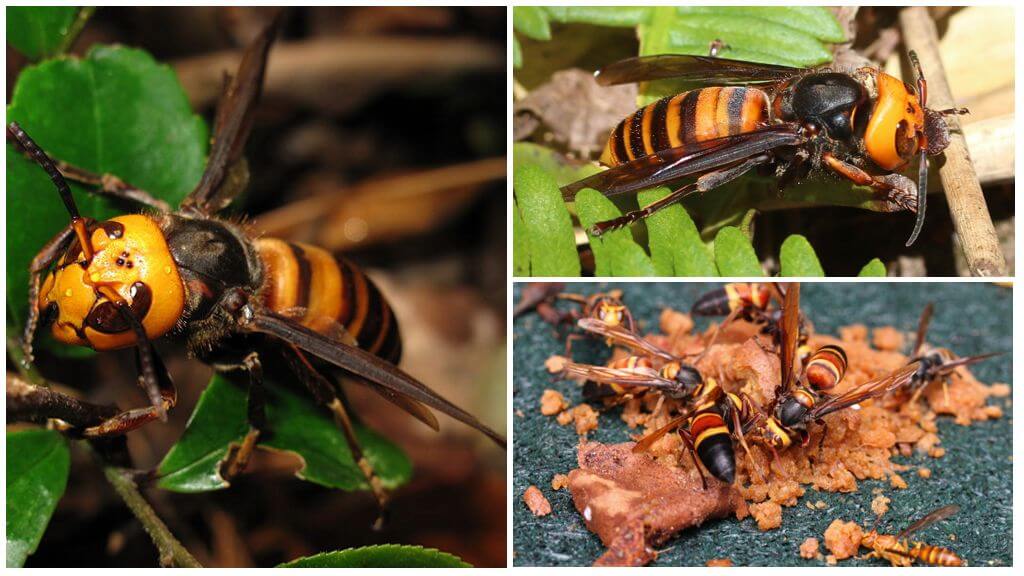
- Outwardly, the giant is very similar to a wasp: it has a segmented body with yellow-brown stripes, a black chest. On the head of the yellow-orange color are two large eyes and three additional accessory eyes. A photo of the Japanese hornet is presented below.
- Another characteristic feature of the insect is its powerful jaws, with the help of which the Japanese hornet is able to harm even a larger enemy than himself.
- The main weapon of the giant is a very long sting (more than 6 mm). With its help, the Japanese hornet deals a painful blow, letting in a poison possessing a nerve-paralytic effect. Moreover, only females have this organ.
On a note!
The strongest venom of the giant is even capable of causing a serious allergy with a single bite, anaphylactic shock develops in some victims. The consequence of mass attacks of representatives of this species can be various hemorrhages and tissue necrosis.
The lifestyle and nutrition of the Japanese giant

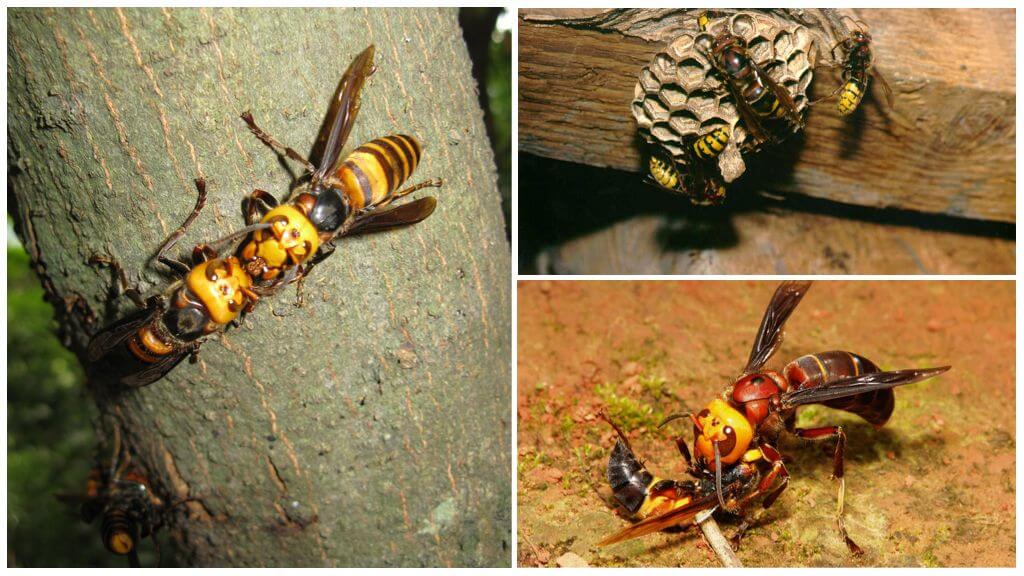
Each individual in the hive has its own responsibilities. The queen uterus, the continuer of the genus, occupies the “leading position”. Food delivery is done by hornet workers. Going in search of her, working individuals can overcome several kilometers.
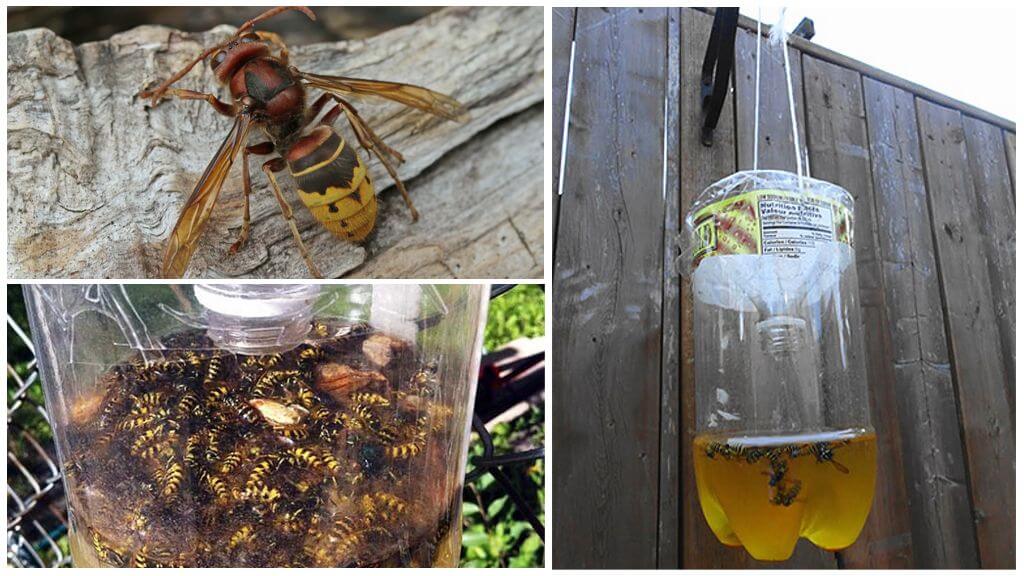
Food for giant hornets is not only fruits and sugar-containing vegetables, but also insect pests of crops, as well as honey bees. Having discovered a bee hive, the hornet marks it with an odorous liquid, which allows him to subsequently return to the find with his brothers. During the attack, the giants literally dismember the body of their victims, trying to extract valuable meat from them. Having dealt with adults, tyrants take larvae and honey, which also serve as food.
Interesting!
It takes no more than a minute for the Japanese hornet to exterminate up to 4 dozen bees. In 3 hours, 3 dozen individuals can destroy the entire bee family.
Where the giant hornet lives
By the name of the insect, it becomes clear that the birthplace of the huge Japanese hornet is Japan. Outside this country, a giant can only be found in the southern part of Sakhalin Island. When choosing a habitat, insects prefer quiet, cozy places, building nests in hollows and on tree branches, in cracked rocks and under the eaves of buildings. The giant hornet's cocoon is very similar to vespiary, from the last it is distinguished only by large dimensions.
How to breed
In the spring, a fertilized female builds a nest from the bark of branches, which she crushes with her powerful jaws. The queen uterus moistens wood particles with the secretion of the salivary glands, as a result of which the composition takes the form of rough paper.
Of the 3 hundred eggs laid by the female after 7-10 days, larvae appear. After three links they pupate. A month later, a young hornet emerges from the pupa. It can not only independently find food for itself, but also take care of the appeared larvae.

Interesting!
In unfertilized eggs exclusively males develop. Future successors of the genus occupy more spacious and comfortable cells.
With an increase in the number of individuals in the family, the dimensions of the nest also increase. Young individuals begin mating, future queens of the uterus go in search of a favorable place for the construction of the nest, and males die with the approach of cold weather. With the arrival of heat, the females wake up and begin building a new shelter.
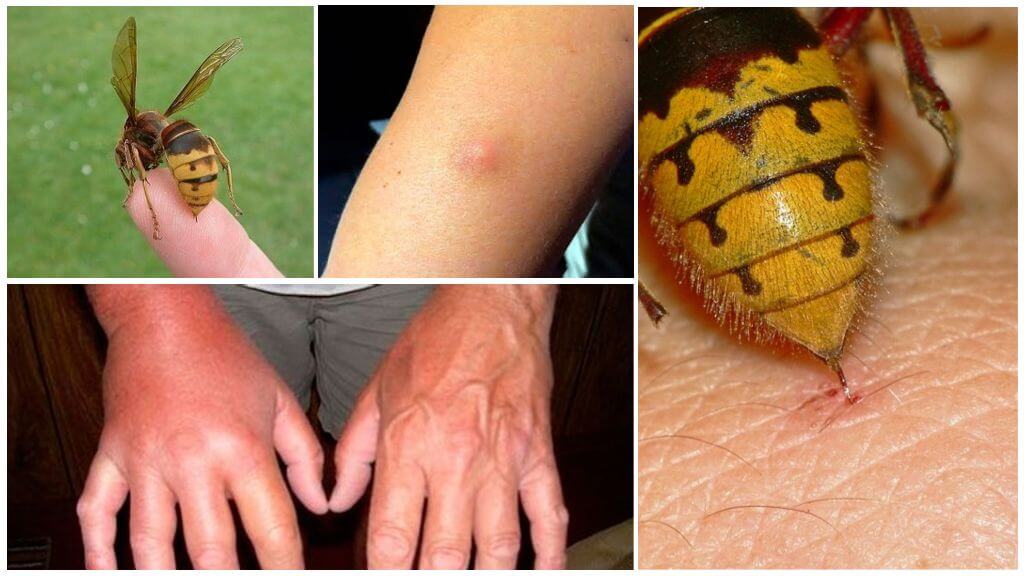
Bite symptoms
Japanese hornet bite is accompanied by:
- strong pain;
- the occurrence of extensive redness and swelling in the area of damage to the skin;
- palpitations and headache;
- high body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes;
- shortness of breath and nausea.
Gigantic hornets are able to repeatedly sting their prey, and for this they do not necessarily sit on the skin.
The ingress of histamine (an allergy-causing compound) into human blood is especially dangerous for hypersensitive people. Therefore, they urgently need to provide medical assistance.
Important!
Pre-medical actions consist in applying a cold compress to the site of the bite and taking an antihistamine.
What you should know
In order not to become a victim of the Japanese hornet, it is necessary to observe basic precautions:
- when meeting with an insect, you can not swing your arms and make sudden movements, trying to drive it away from you;
- no need to try to catch or kill the Japanese hornet, since after this the offender is unlikely to be able to avoid the attack;
- In no case should you destroy the nest of dangerous insects.