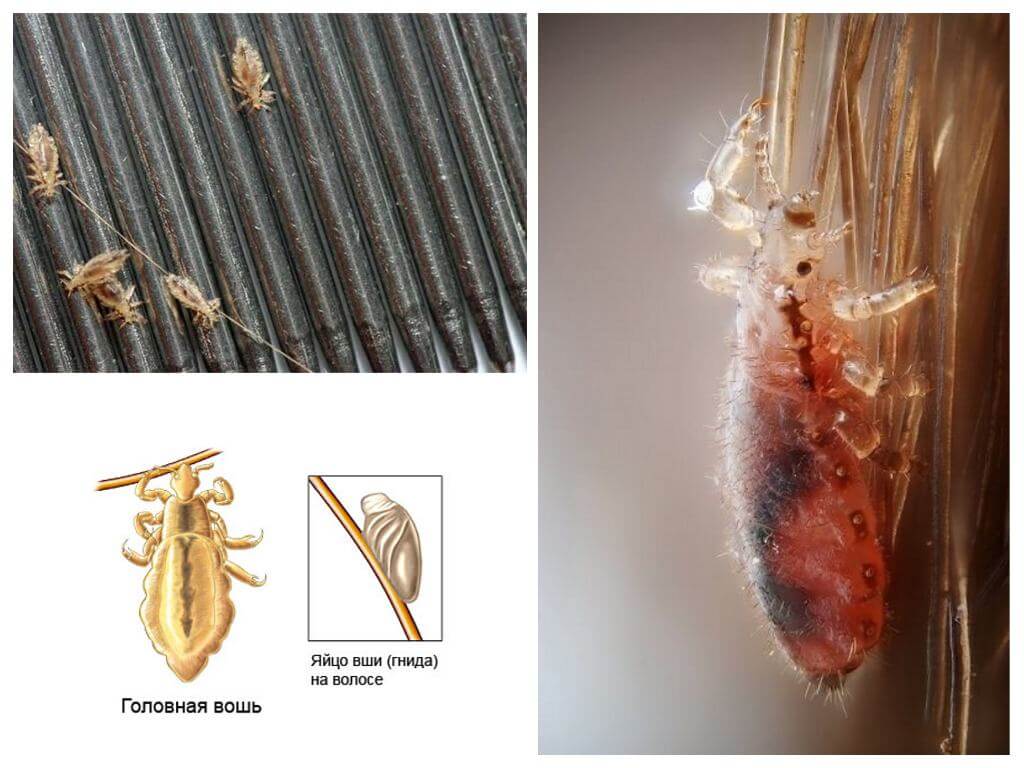
- Lice and Nits
- Nits
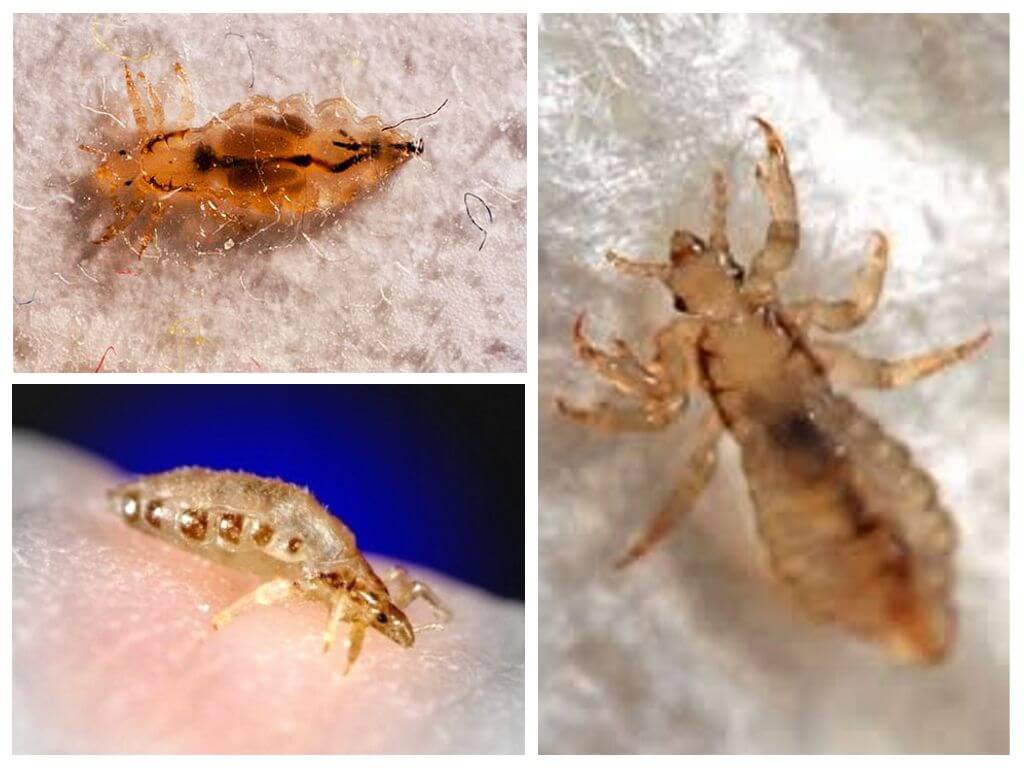
- Lice
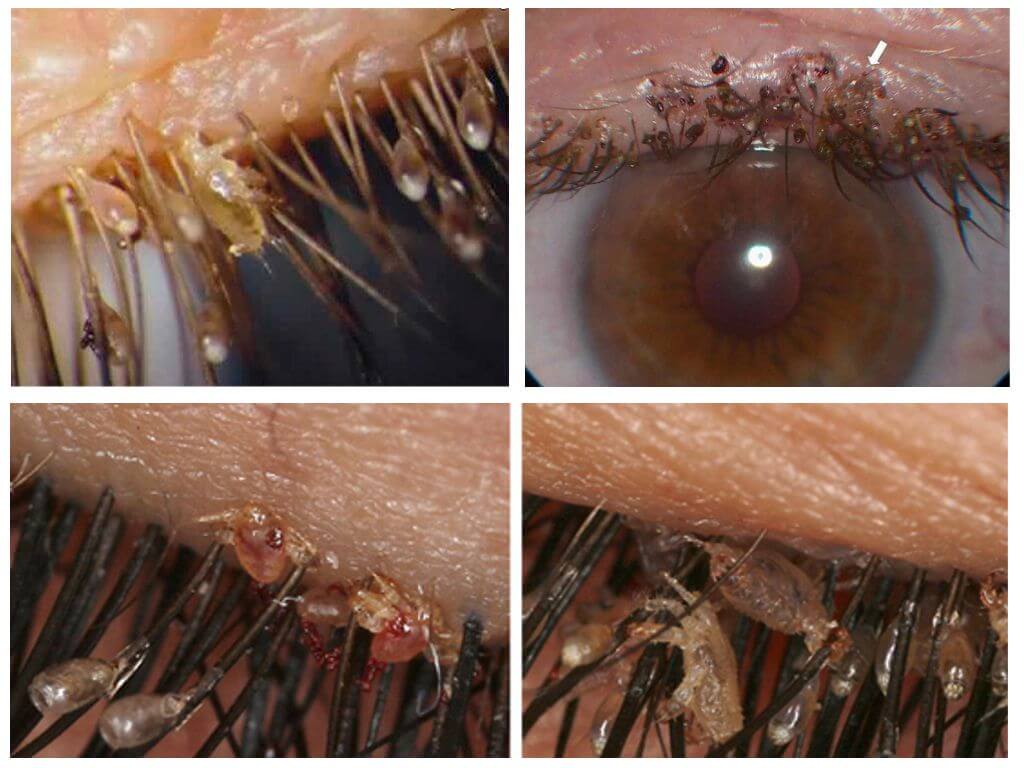
- Pubic lice
- Linen lice
Pediculosis - a parasitic disease that affects the speed of development, the extent of infection. The source of the disease is louse. The insect parasitizes exclusively on humans, the entire life cycle takes place on the body. In nature, there are several human lice - head, body, pubic.
Lice development
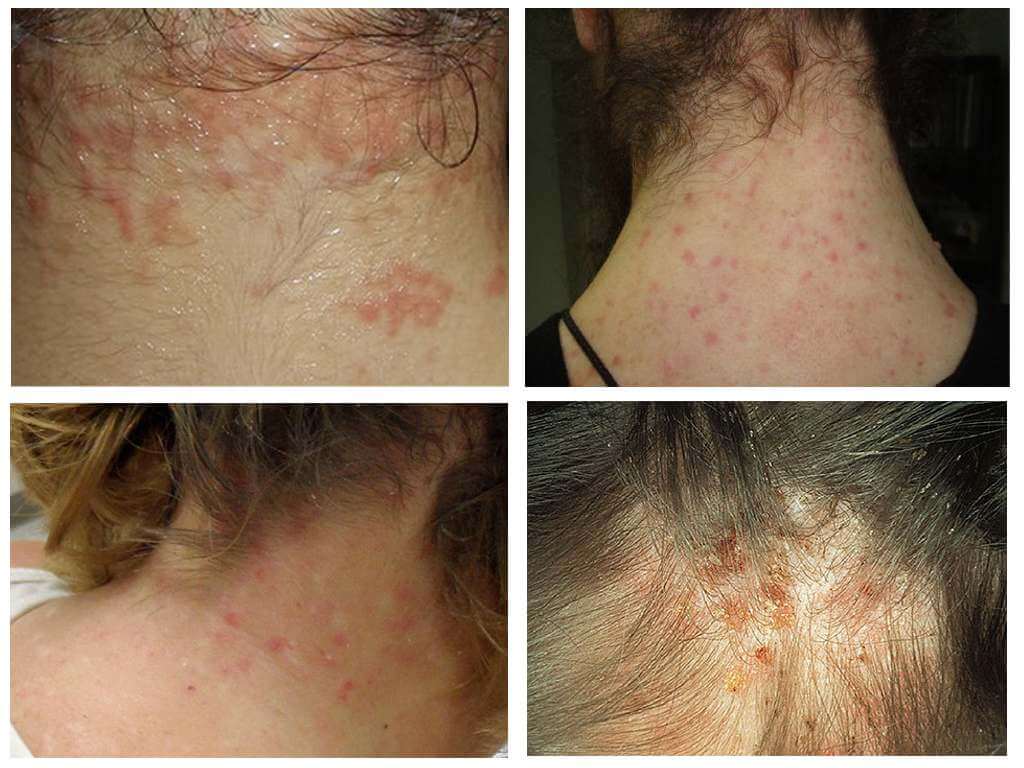
A person becomes infected with parasites in close contact with the patient, his things. At first, the insect does not give itself away, since itching from lice bites appears after a while.
Interesting!
The skin irritation is not caused by the bite itself, but by the saliva of the parasite. In order for an allergic reaction to occur, a certain amount of allergen must accumulate. This usually occurs within 5 days.
The first thing that a female does on a person’s head is to lay eggs. The life cycle of head lice and nits is 16 days. After leaving the egg, the larvae immediately begin to parasitize. Their food occurs every 2 hours. Itching begins to occur, pediculosis takes on a pronounced form. An adult female eats every 4 hours. To get enough, she needs a minimum amount of blood. Nutrition is necessary to replenish vitality, reproduce offspring.
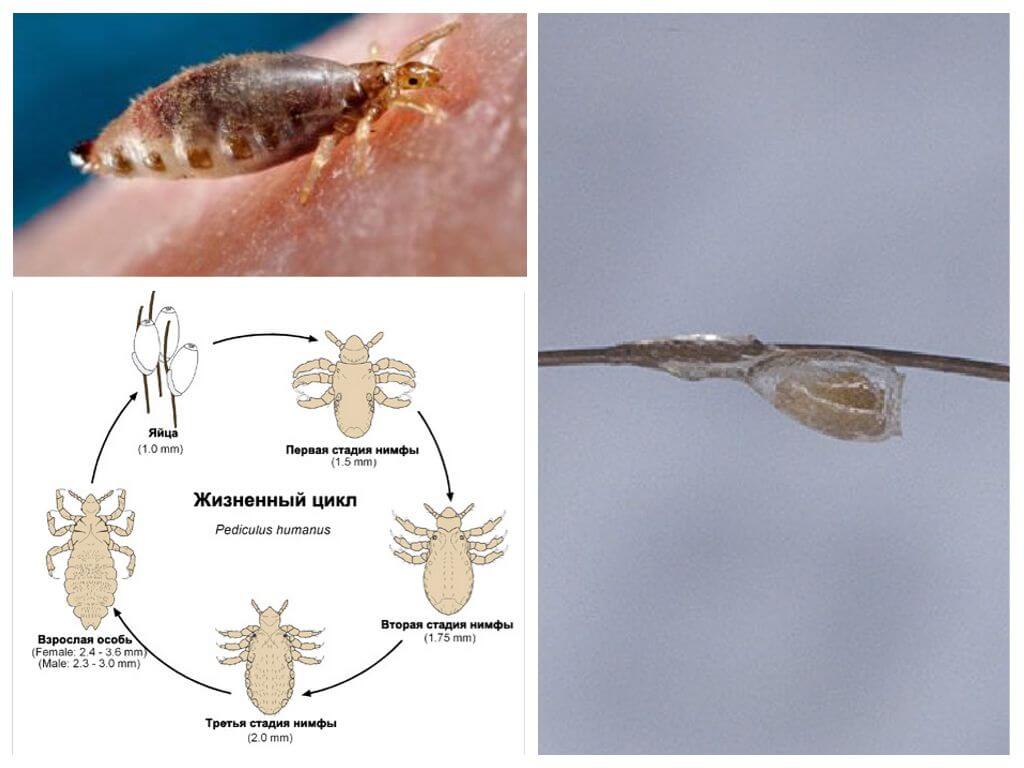
They multiply rapidly after infection. Every day, the female lays about 4 eggs. Incubation period does not differ in duration, therefore, within 1 month a large population of parasites appears on the human head. The patient becomes a pediculosis peddler, his whole life turns into a real nightmare. Lice are transmitted with hugs, close contact with the head of another person.
Egg cycle
Lice refers to insects with incomplete conversion. In her life, there is no stage of the larva, which differs in appearance and nutritional characteristics.
Patients are always interested in the question of how many eggs one louse lays, as infection occurs very quickly. An adult begins to produce offspring a few hours after mating. 2 to 4 eggs appear daily.
Breeding lice is an entertaining process. The seminal fluid of the male fertilizes all the eggs of the female. One mating is enough for a female to lay her entire eggs short life. The female does not need a partner to continuously produce offspring - this is why females lay so many eggs.
Lice fix eggs - nits at the base of hair roots. At a distance of 1 cm, by the location of the nits in the thread, one can determine how long the eggs were laid. Initially, sticky mucus comes out of the genital organs of lice, followed by an egg. The substance hardens, provides reliable fixation to the nits. It can not be removed when combing with a regular comb, rinse with shampoo, other hair care products, which is very distinguishes nits from dandruff.
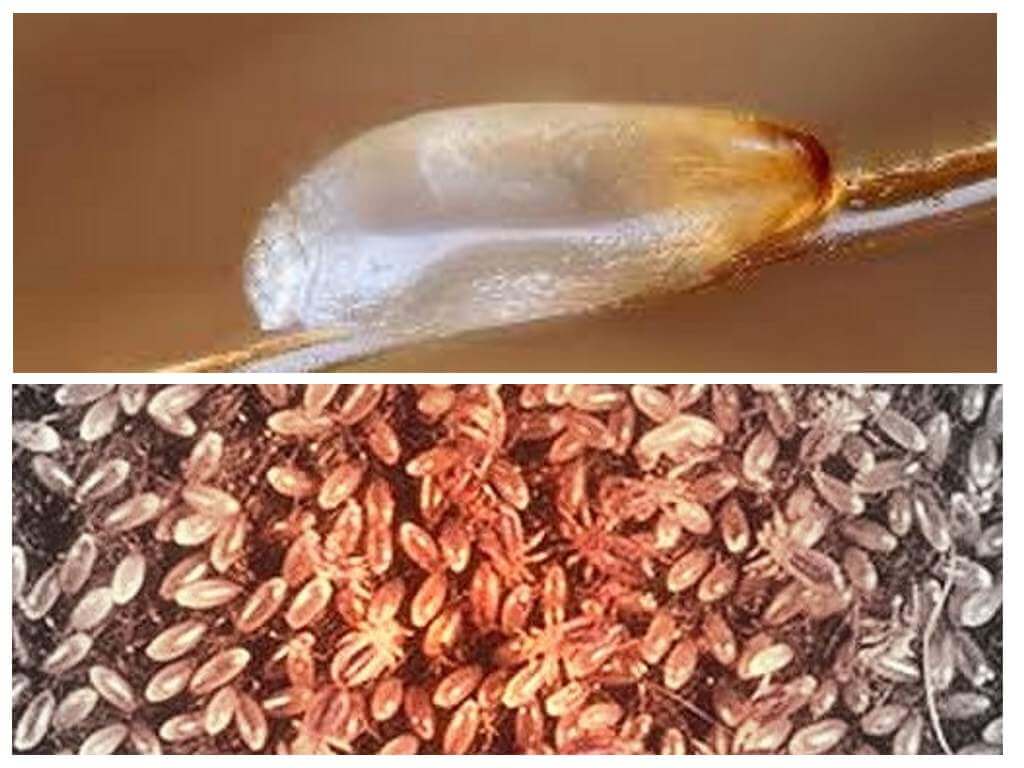

Interesting!
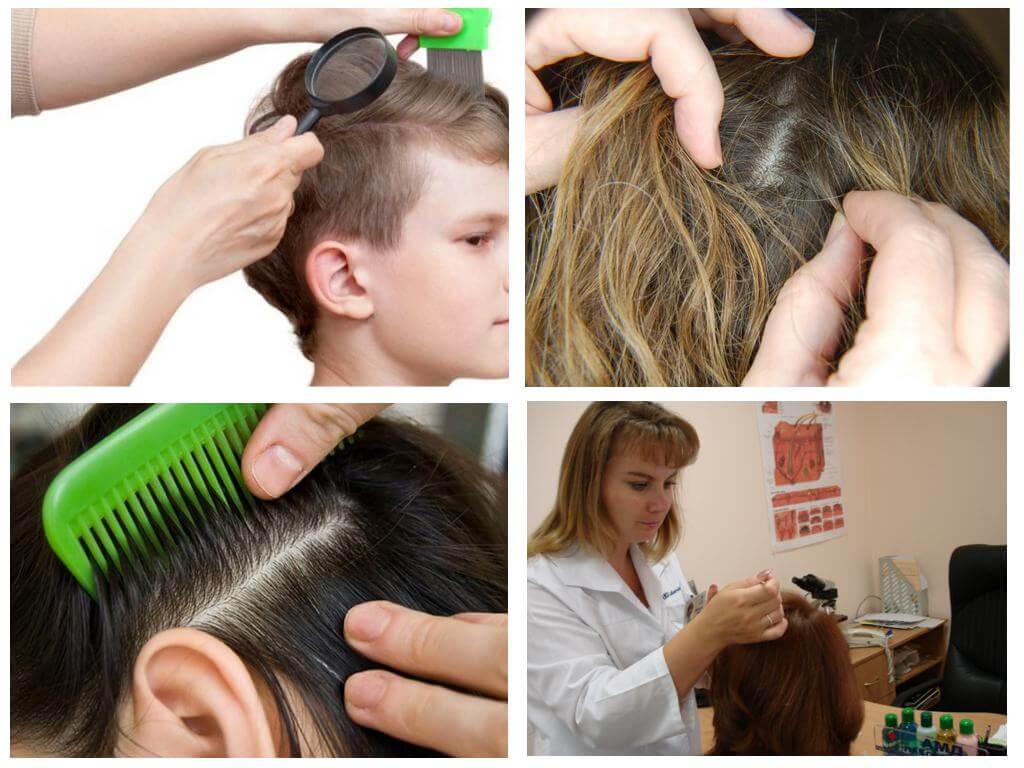
The shell of the nits is so dense that it does not pass a single insecticide. The larva develops safely after a "heavy attack." The only method to control the larvae in the shell is combing nits. For these purposes, use a comb with a fine pitch or special lice comb.
Fast larval development stage
An insect develops in an egg for about 8 days. The formed individual gnaws on the shell, but cannot get out. It begins to actively inhale air, to release through the rear hole.Carbon dioxide accumulates at the bottom of the egg, which pushes the larva out. Lice of a new generation appear - nymphs.
Interesting!
The larva in appearance is no different from the imago. The recent appearance of the body gives her size.
No less curious is how quickly head lice breed. Immediately after leaving the egg, the larva begins to feed. Every day the body grows in size. The chitinous shell remains unchanged. To get rid of him, the nymph simply dumps him. After a few hours, the upper shell of the body hardens. The young individual regains its former form, but differs in large size.
In total, the larva undergoes 3 molts. Development with transformation lasts 8 days. At the last stage, the nymph forms the genital organs. The insect turns into an adult - an adult. New parasites instantly begin mating.
Stage of development of lice:
- nits - about 8 days;
- larva before molting - 3 days;
- 1st generation nymph - 2 days;
- 2nd generation nymph - 3 days.
The timing of the development and reproduction of lice depends on the availability of a food source, temperature. Under adverse conditions, the process is extended to 20-30 days.
Adult Lice Life
The adult lives 30-42 days. Throughout his life he lays about 140 eggs. The short lifespan of lice is due to the constant availability of food, comfortable temperature conditions.
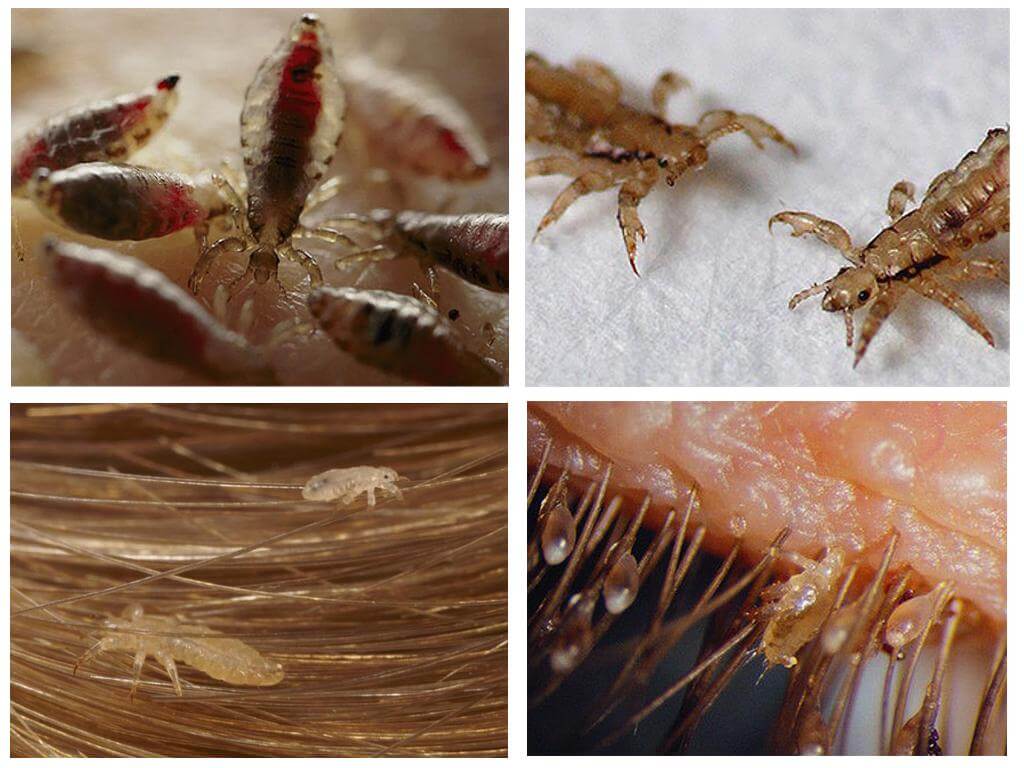

Lice never starves, there is always the opportunity to drink blood. No time is wasted searching for a partner. One mating is enough to reproduce offspring all life. Comfortable temperature for existence and development is within 31 ° С. On a person’s head, the range is always maintained at any time of the year.
The louse breeding season is adjusted if the louse creeps onto another person’s head or is on a pillow or headgear for some time. Outside the human head, an insect can survive 3 days.
Head louse not able to parasitize on other parts of the body, infect animals. Pediculosis is transmitted only by a lousy person, his hats, combs. The development of lice and nits occurs imperceptibly for humans. Their existence on the head gives out a constant itch, which intensifies in the evening. A strong male who dies a week after mating is able to breed and give offspring.
Interesting!
In ancient times, the appearance of lice was considered an infection. It was assumed that parasites developed for a long time under the skin, and when exposed to favorable factors, crawled out. This explained the rapid breeding of lice.
Other types of human louse
In addition to head lice, there is a clothes or clothing, pubic. The latter was called the ploschita.
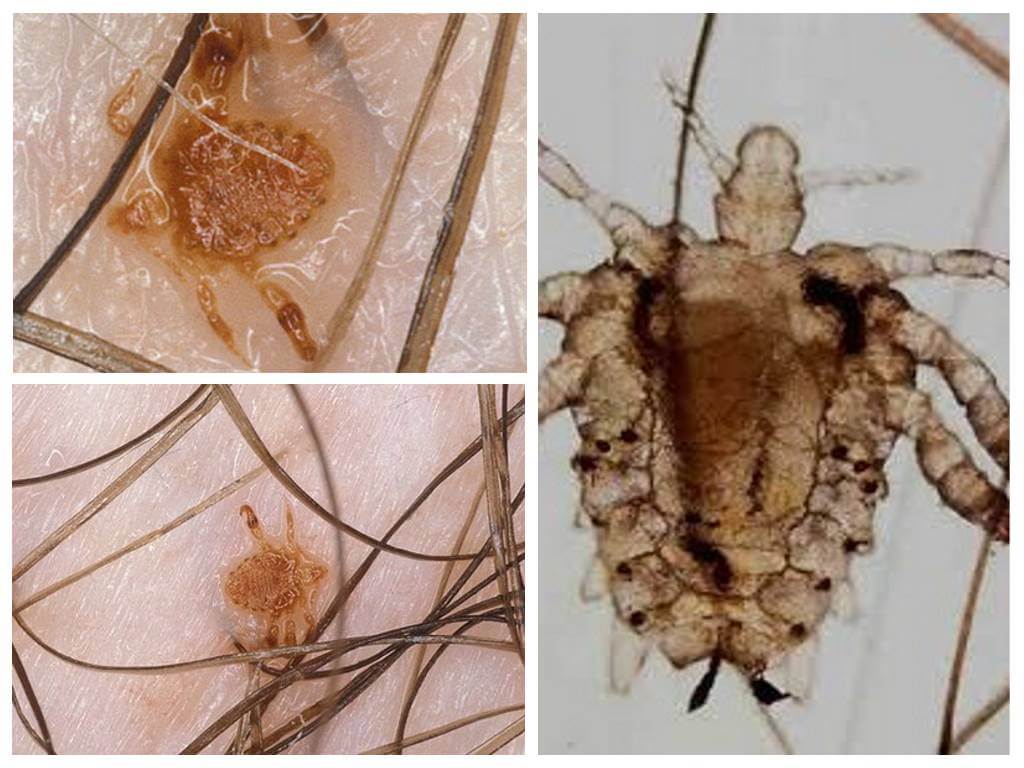
- Pubic Louse differs from the head appearance - more like a small crab. Parasitic on the pubis. With severe infection, the surface is found in the armpits, on the eyebrows, on the eyelashes. The hair on the head does not fit in structure. Infection occurs during sex, in contact with towels, personal items. Parasites breed quickly. The female lays about 7 eggs per day. Pubic lice manifests itself within 2 weeks.
- Cootie practically does not differ from the head one. Repeats the entire life cycle, especially reproduction. The only difference is the habitat - the personal belongings of a person, bedding. Parasitizes on the body, except the pubis, head. Able to live without food for about 5 days.

How lice reproduce has been known since ancient times. Well studied where do the parasites come from. all paths of infection. Get rid of lice possible for 1-2 procedures. Pediculicidal drugs You can buy in a pharmacy or use folk remedies. At risk are children, dysfunctional families, people with no fixed abode. In the absence of treatment, infection gets into the wounds from bites, complications develop.





Until now, I thought that nits were killed by insecticides. It turns out that no, you need to work hard to comb out the hair. I have a hairstyle from long hair, I don’t really want to cut it. By type of activity, I often travel on business. You can get pediculosis for one or two. Each time I return home I ask my wife to check her head. I'm afraid of these creatures.
I understand you very much. I myself have such a problem with business trips. Once lice picked up. I did not notice them until my head began to itch. I asked to see my friend, there a whole crowd runs around. I was at a loss where so many came from, why I had not noticed the presence of parasites before. They breed, of course, interestingly. But that makes it scary. I'll take it into service.
It was interesting to read about the development of parasites. Faced with them in childhood. It seems that they appear suddenly and immediately in large numbers. I remembered now that I was crawling on the head of something or someone, and the itching appeared a week later.
As soon as nature is created interestingly! Once mated and reproduce all their life offspring. Until recently, I thought that for each clutch of nits, the presence of males is required. It turns out that the situation is much simpler.
Yes, I was also at a loss how pediculosis develops so quickly. One female is enough that in a month the whole head is teeming with these creatures. And withdrawal is not so simple. If there are 2 nits left with a female and a male, everything will go in a new circle.
I learned a lot of interesting things for myself. I’m not particularly interested in parasites, but in the kindergarten where the daughter goes, lice were found in the child. I had to study in detail the reproduction of parasites, the development of pediculosis, so as not to miss the time.
Cognitive, informative article. I learned a lot of interesting things for myself. Particularly struck by the process of turning nymphs into an adult. For a week, each of them is able to reproduce offspring.
I, too, have always been surprised at the rate of parasite reproduction. I remember my feelings in childhood. Infected with pediculosis in primary school. I felt something creeping, then a terrible itch. Mom brought them to me with laundry soap, tearing nails from her hair with her nails. The procedure is terrible, unpleasant. Now I understand why she was afraid to miss at least one nits.
Remained impressed by the read. Even outside the head, the louse can calmly be on the pillow, wait for the victim. Hitting a new head, he immediately gets down to business, and she does not need a male at all. Since fertilization has already happened once.
I always thought that louse from the head with a strong infection gets to the body. It turns out that this is not so. A completely different kind. Rapid breeding is terrifying. It is difficult to imagine what is happening on the head if nothing is done. Poor children from dysfunctional families and homeless people! But, in general, not a single person is safe from this scourge. On a clean head, parasites live and breed more willingly than on a dirty, groomed one.