- Diseases derived from mice
- Rodent-borne diseases
- Disease prevention
The neighborhood with small rodents such as mice and rats is very dangerous for human health. Therefore, it is necessary to know in advance what diseases the mice carry, how the symptoms of these diseases appear and what needs to be done.
Methods of transmission of infection
Like many wild animals, mice are carriers of various infections and diseases. How dangerous are the mice in the house, settled in the kitchen or in the basement, whether a person can get the disease from them - the answers to these questions will make many think. Indeed, from rodents, a person can become infected in various ways:
- consuming water or food that may be contaminated with feces from a sick mouse;
- inhalation of dust with wool or mouse droppings;
- contact with the corpse of a rodent;
- when a person bites a mouse;
- through parasites that live in the wool of mice;
- infection through the respiratory tract when in a room where there is an accumulation of rodents.
What can be infected from mice
Diseases transmitted to humans from mice can be very dangerous and even cause death. Many centuries in a row mice and rats carried dangerous diseases plague and typhoid. However, in the 21st century, these terrible infectious diseases almost never occur. But the list of what can be infected from mice, i.e. infectious and parasitic diseases are still quite long.
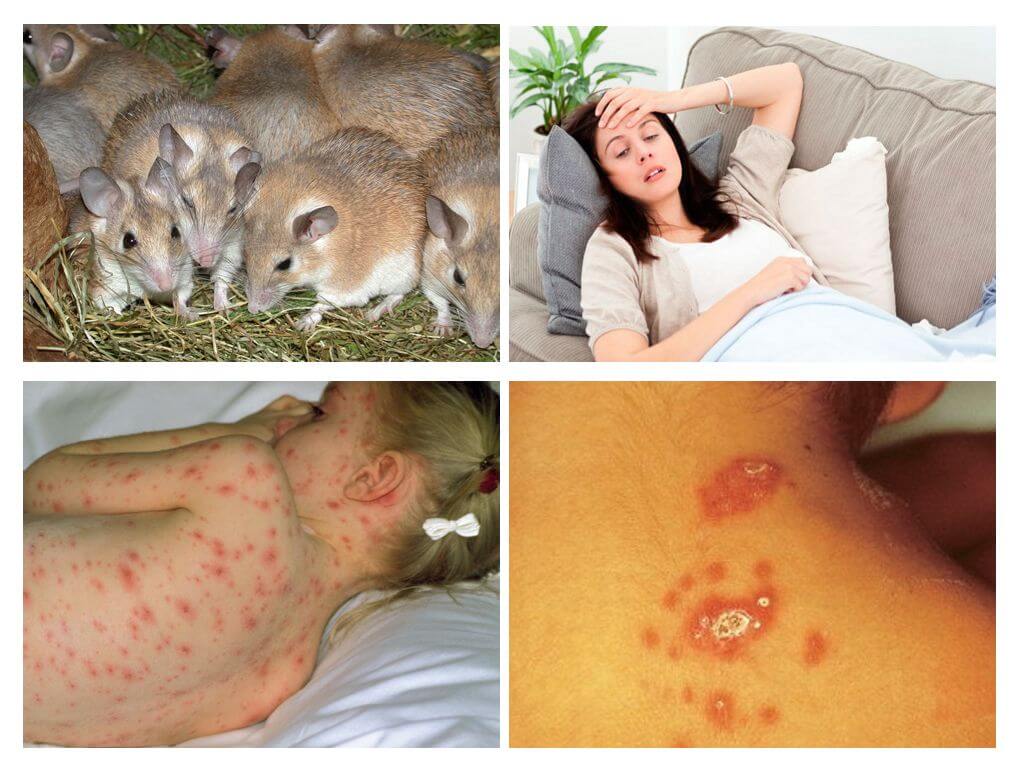
Salmonellosis
Salmonella bacterial disease. A person can become infected through mouse droppings or by eating contaminated food. Mice are carriers of salmonella, they can transmit it to pets, and an infected person can spread this bacterium to healthy people.
Symptoms of the disease are similar to signs of intestinal disorders:
- within 6-48 hours after infection, dizziness and fever appear;
- vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea;
- liver and heart failure, urinary tract infection and even toxic toxic shock can develop very quickly.
Salmonellosis is now successfully treated with antibiotics, however, there are such forms that require prolonged treatment and recovery from the disease.
Leptospirosis
The causative agent of the disease is the bacterium Leptospira, which is transmitted through the urine of sick animals into the ground, water. This kind of infection is tolerated. different types of mice, wild rats, cats, dogs, livestock and some wild animals. A person can become infected after direct contact with a mouse - the carrier of the disease, when swimming through water or dirty foods.
Leptospirosis is deadly for humans, most often it occurs in countries with tropical and temperate climates.
Important!
On the territory of Russia annually in the summer, several dozen cases of infection with leptospirosis are recorded. The leptospira bacterium can maintain its viability for several weeks in water and soil under favorable conditions: high humidity and heat.
The clinical symptoms of the disease usually appear 2 weeks after infection:
- fever;
- joint and muscle pain;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, redness of the eyes;
- nausea and vomiting;
- inflammatory process in the kidneys, sometimes in the brain.
Treatment of leptospirosis is possible only in a hospital under the constant supervision of specialists, otherwise a serious complication may occur - Weil’s disease, which manifests itself in renal and liver failure, possible bleeding and cerebral edema, which can lead to death.
Tularemia
This disease is transmitted from mice to humans through blood-sucking pests: ticks and fleas that live in their hair. Having bitten a person, the tick gives him an infection that is caused by the bacteria Francisella tularensis. In rare cases, tularemia can be transmitted through raw meat, causing mouth ulcers.
Signs of the disease: ulcer at the site of an insect bite, fever, swollen lymph nodes, in severe cases - chest pain, cough and breathing problems.
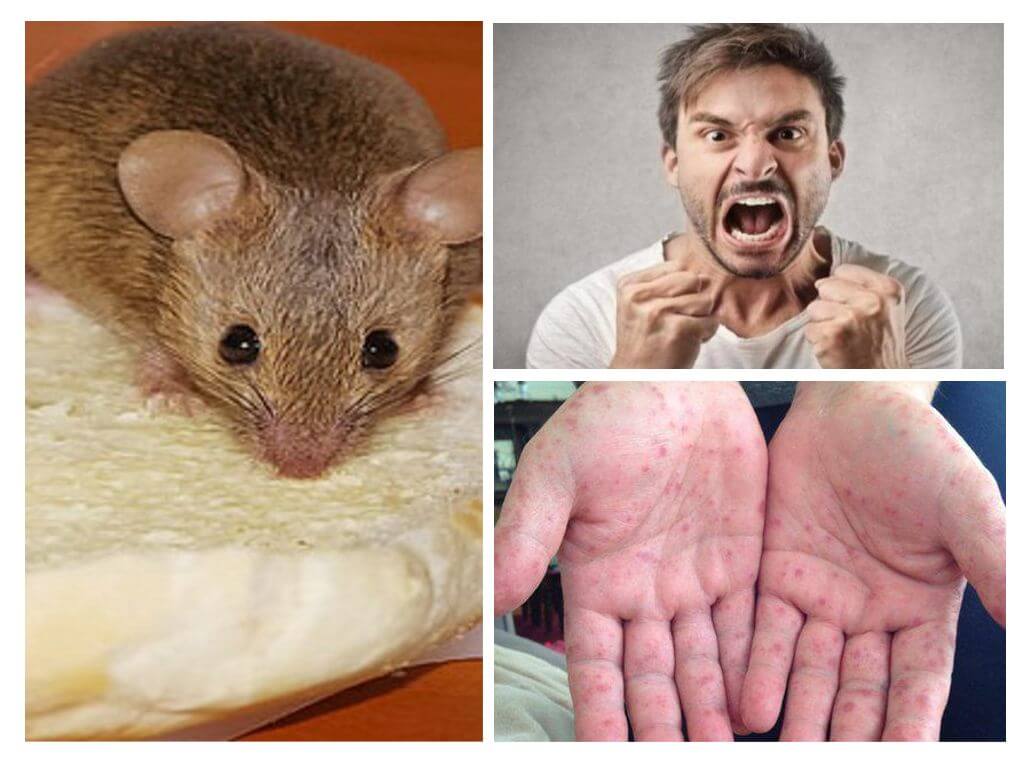
Hemorrhagic fever
This disease belongs to the most severe types, 5% of sick people according to statistics die. Natural foci of infection are found in the Far Eastern regions of Russia and China. A fever is transmitted to a person by inhaling dust, in which there is an infection from a large amount field mice and rats while working in the fields or at a construction site. Sometimes infection can occur through food contaminated with mice.
Distinctive signs of the disease: headaches, fever, digestive upsets, insomnia, severe thirst, redness and swelling of the face, possibly hemorrhages on the skin, kidneys are severely affected.
On a note!
Nearly half of people who have had mouse fever are subsequently forced to treat severe complications in the heart, lungs, and brain.
Yersiniosis
Another name for the disease is pseudotuberculosis, which is ubiquitous and occurs in Russia in the Far East. Yersiniosis is very difficult to diagnose due to a wide variety of clinical manifestations.
The causative agent is eirsinia - a bacterium that settles on fruits and vegetables, perfectly withstands frosts, dies only when boiled. The disease can be picked up from wild and domestic rodents through urine, mouse and rat droppings.
Important!
Outbreaks of pseudotuberculosis are regularly recorded from the end of winter to the beginning of spring, most often the bacteria multiply well in warehouses and vegetable stores with high humidity.
Symptoms of yersiniosis can occur after 20 days: weakness and fever, pain in the muscles, abdomen and joints, sore throat, decreased appetite, digestive problems, skin in the upper body is covered with acne.
Tapeworms
These parasites live in the body of mice and rats, can be transmitted through food or water, which came into contact with mouse feces. The eggs and larvae of the worms penetrate the human digestive system, become adults and begin to multiply, which negatively affects human health.
Rabies
This disease is deadly for humans and animals. Rabies in mice and rats is extremely rare due to the fact that the bite of another animal ends in his death. Most often, rabid animals are found in the wild: foxes, raccoons, dogs, wild cats. However, bats are quite capable of becoming carriers of such a disease. If after a bite of an animal a person develops symptoms of brain inflammation, then we can talk about rabies infection.
Prevention of infection from mice
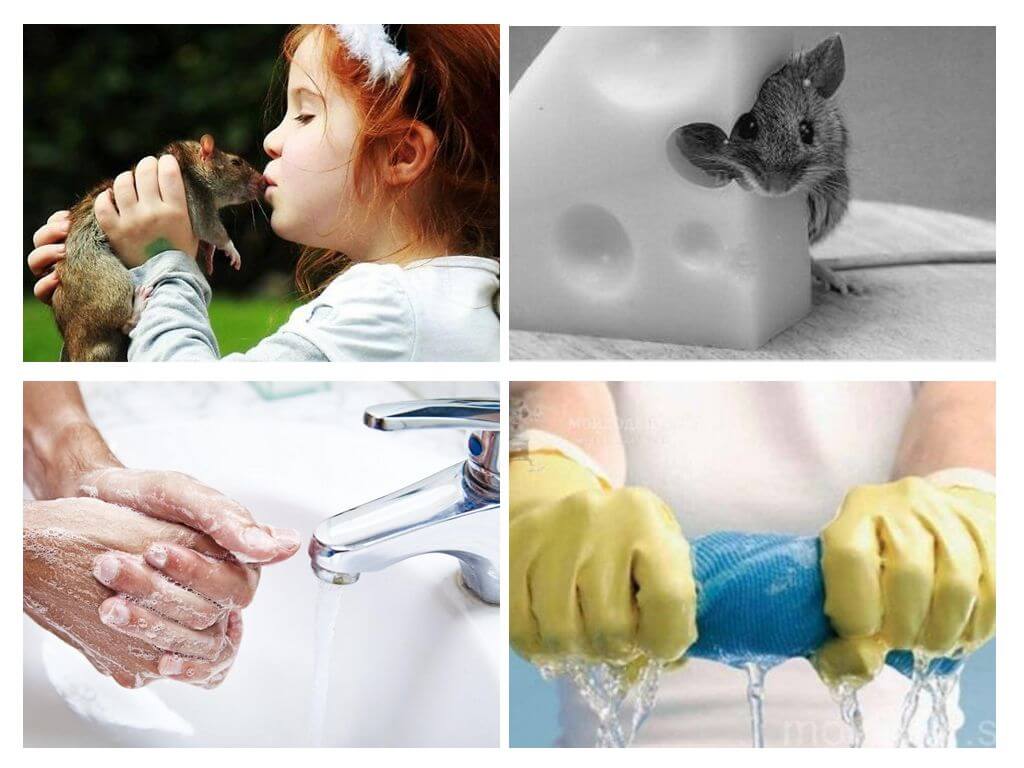

When even one mouse appears in an apartment or a house, each person must understand the danger that threatens him. After all, mice not only spoil food products, furniture, but also carry various infections: bacteria, viruses, infections.
Therefore, compliance with preventive measures in order to reduce the risk of infection of the landlord is very important:
- it is better for a person not to contact with rodents and their feces;
- work in rooms where mice may be located is carried out only in protective clothing, later it must be burned or disinfected;
- it is strictly forbidden to eat foods that have traces of the presence of rodents;
- products should be stored indoors or in containers inaccessible to pests;
- be sure to wash your hands before eating;
- carry out wet cleaning using disinfectant solutions;
- prevent the accumulation of garbage and waste in the country, at home and in the apartment;
- carry out the destruction of settled rodents;
- Do not swim in natural waters, especially not very clean;
- control cleanliness indoors and in food storage areas.