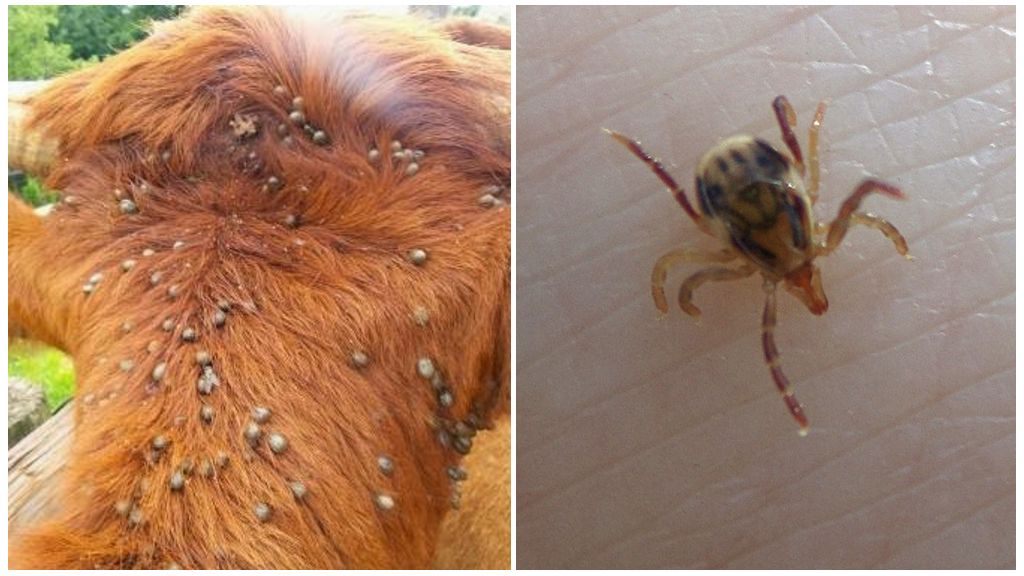
- Ticks in cows
- Removing a tick from a cow
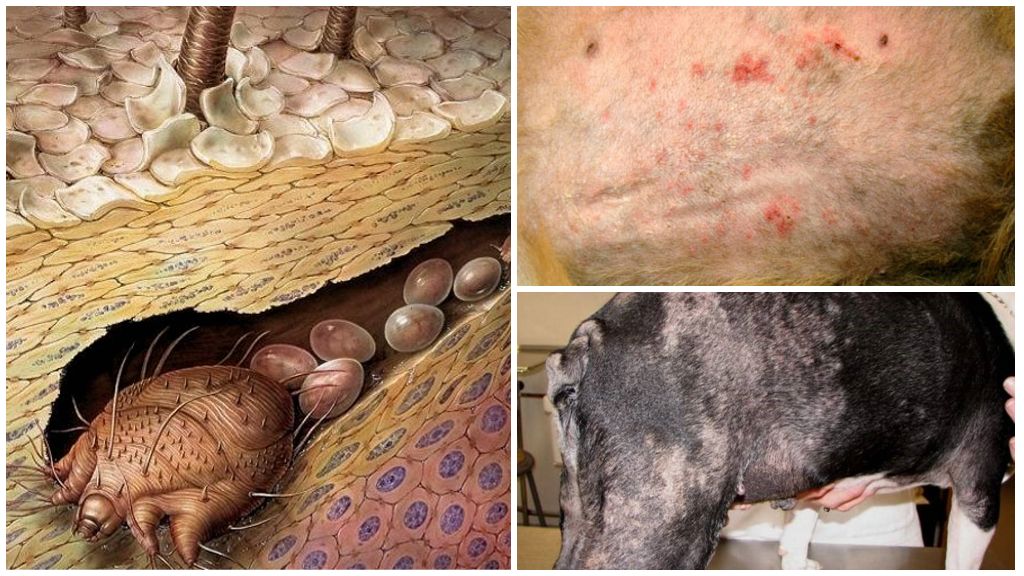
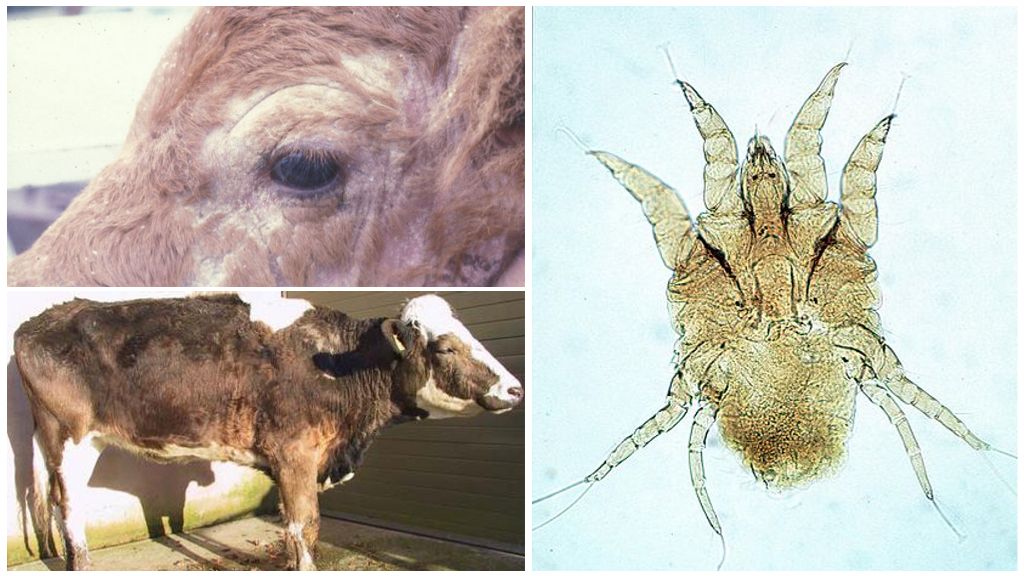
- Psoroptosis
- Demodecosis in cows
The consequence of bites and the actions of various types of ticks on cows is a lot of unpleasant diseases: psoroptosis, demodicosis, chorioptosis and others. Is it possible to drink milk if the cow was bitten by a tick and how to treat the animal - the answer to the question will be of interest to those who keep cattle at home (cattle).
Tick Bite Disease
Blood-sucking parasites of which are ticksare often carriers of dangerous diseases. As a result of a bite, they can infect cattle with diseases such as foot and mouth disease, brucellosis, tularemia, anthrax, etc.
The most dangerous diseases that ticks carry are:
- pyroplasmosis, the causative agent of which are unicellular microorganisms of theileria and babesia; these protozoa penetrate the blood and infect red blood cells;
- psoroptosis is a skin disease of cattle, characterized by the development of inflammation of the upper layer of the epidermis, baldness and weight loss of the animal;
- encephalitis, which is dangerous for humans, is transmitted through blood, etc.
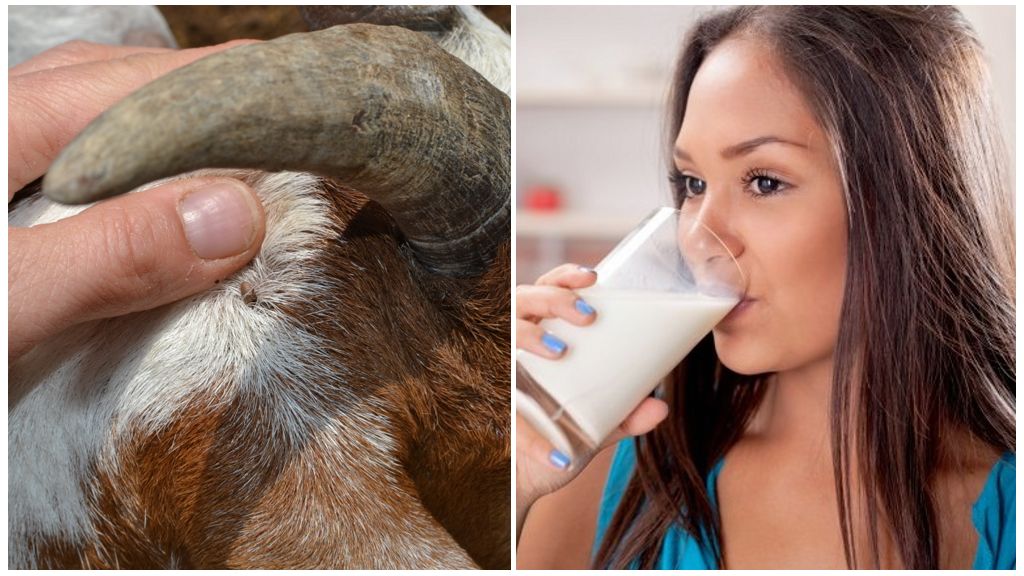
In case of untimely detection of dangerous diseases, there is a danger to the life of cattle, as well as to human infection through milk. The question of whether it is possible to drink milk if the cow is bitten by a tick is very acute. Since it is about the health and life of people.
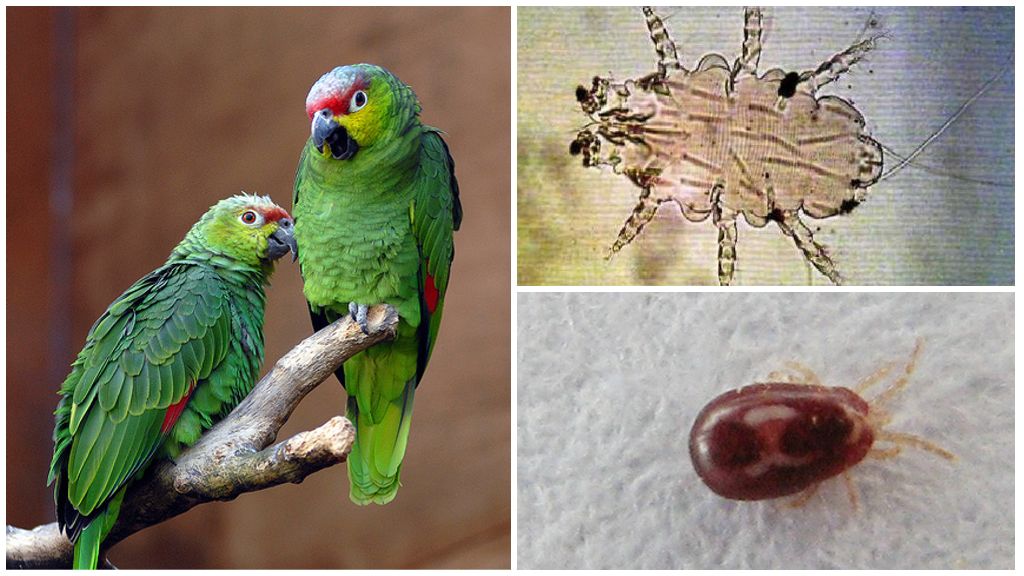
Types of Ticks and Disease
Scientists have a total of 55 thousand species of ticks, the size of which can be from 0.2 to 5 mm. These arachnids are distinguished by a strong shell and a special structure of the mouth, designed to suck out blood. They are attached to the body of the animal with the help of a special organ - the terminal segment, which has claws and suction cups. At first, the tick pierces the skin with the help of claw-shaped appendages, and then it penetrates into its upper layer near the blood vessels and begins to drink blood.
The most dangerous types of ticks and diseases:
- ixodic view - transmits encephalitis;
- scabies mite - causes demodicosis and scabies;
- subcutaneous - penetrates under the skin, which causes severe itching and torment for the animal;
- nakozhnik - a type of tick, the causative agent of psoroptosis;
- ticks that cause cattle chorioptosis settle on some parts of the animal’s body.
Pyroplasmidosis: Symptoms
The incubation period of the disease is 2-3 weeks after a direct tick bite. Symptoms of pyroplasmidosis are bright and acute:
- body temperature rises to +41 + 42 ° C;
- the state of the animal is depressed;
- appetite and chewing gum worsen;
- mucous membranes turn yellow;
- after 2-3 days, the color of urine changes to pink, later it becomes dark red;
- milk also changes color to reddish and begins to bitter.
After infection, the cow has a digestive function disorder and the liver suffers, while the pregnant woman may have a miscarriage. The prognosis of the disease is unfavorable, because after 4-5 days in 60% of cases the death of the animal occurs.
Diagnosis of the disease can be done in the laboratory: take a blood test for the presence of these microorganisms.
Pyroplasmidosis treatment
The effectiveness of therapy and the life of cattle depend on how quickly drug treatment began. Medicines for cows for ticks: pyrotropic medications: Azidine-vet, Berenil, etc.
In order to prevent bites of cow ticks, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- to protect the cow, you need to use special sprays and emulsions to deter blood-sucking pests that spray the skin of animals;
- grazing cows only in clean pasture areas, for which they should be pre-checked at the beginning of the grazing season;
- after returning from the pasture (during the period of danger of the appearance of "bloodsuckers") all cattle must be carefully examined for parasites and immediately remove the tick, if any.
Important!
Milk from a cow suspected of having a disease can only be drunk after boiling, because the virus can be transmitted to humans.
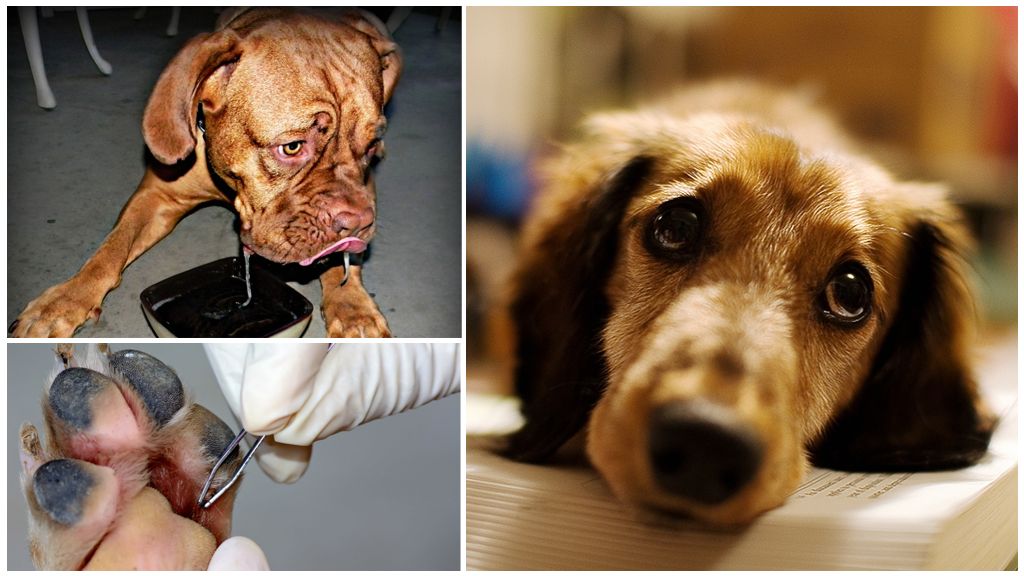
What to do with a tick bite
The cow will not be able to get rid of the tick on its own, so the owner should learn how to do it himself and approach the process responsibly. It is necessary to remove the tick, being careful not to harm the animal, so that the head of the arachnid does not remain under the upper layer of the skin, because an inflammatory process can go on and then the help of the surgeon will be needed.
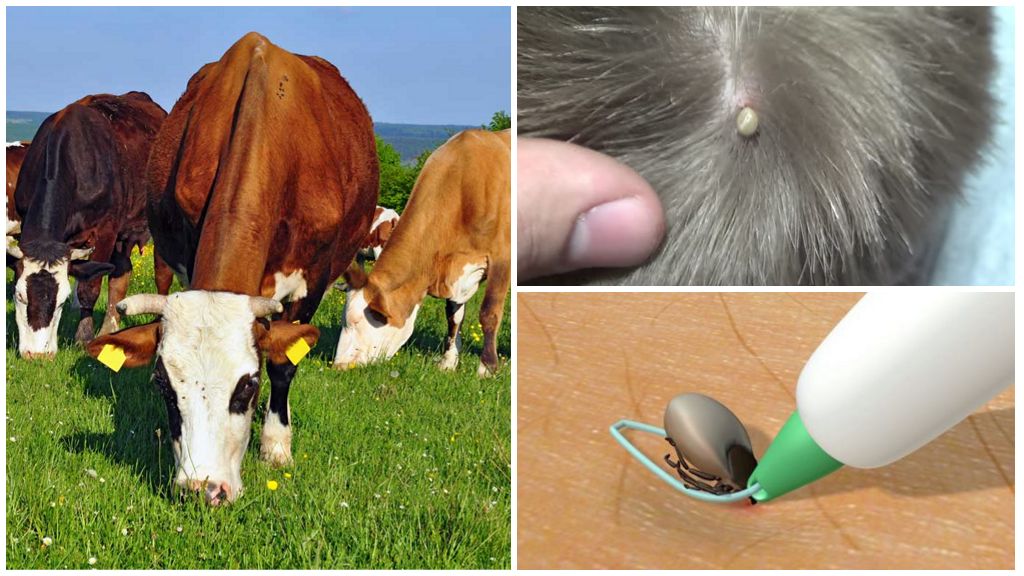
To remove the tick, it is recommended to buy special curved tweezers. With it, you need to grab the body of the parasite close to the bite. Then, rotating in different directions, slowly pull the insect up. Usually, after several turns, it is possible to pull out the tick along with the head and proboscis.
Immediately after removal, grease the wound with green or alcohol. In the field, when the tick is found directly on the pasture, you can use a small piece of strong thread. Throw a loop on the parasite, tighten and begin to twist and stagger to the sides, gradually pulling it up.
Important!
In a situation where a cow or calf has been bitten by a tick, it is strictly forbidden to lubricate arthropod with petroleum jelly or oil to block air to it. With this blockage, the parasite burps the blood back into the wound, as a result of which the rate of possible virus infection increases.
Psoroptosis and its treatment
The causative agent of this disease is one of the types of ticks called the cuticle, Psoroptes bovis (lat.), Which parasitizes in the upper layers of the skin. Its main nutrition is the lymph and intracellular juices of the animal. All stages of tick development occur in the subcutaneous layer of the epidermis.
Cow infection most often occurs through contact with sick cattle. The most favorable period when the cuticle can develop on the body of cattle is from the time of cooling in the fall to the beginning of spring. In the summer months, parasites rarely appear due to bright sunlight and increased immunity of livestock.
On a note!
If there is no cure for the disease, then during the summer period ticks sit and hide in those areas of the animal’s body where light access is minimal (groin, area under the tail, etc.).
The main symptoms of a bite of a tick of a cuticle and signs of the disease:
- thickening or creases appear on the skin of the cow;
- affected areas continuously itch;
- 10-14 days after the bite, an increase in temperature occurs;
- blisters and knots form on the skin, then they turn into vesicles with a liquid that gradually burst, and the liquid spills out;
- hair loss and hair loss occur.
Before starting treatment at home, tests should be done in the form of skin scrapings, after confirmation therapy should be started. To begin with, the animal needs to be prepared - to clean the affected areas of the skin, soften with a soap solution and special oils, remove dried crusts, it is recommended to cut the coat.
Preparations or how to treat a cow from cutaneous ticks:
- Neostomazan and Cidrin, which are added to the solution, are treated in a swimming pool in which the drug is dissolved;
- colloidal sulfur (suspension 2%) and dust (300 g per individual);
- Tiovit, Kosan, Isofen - are used for spraying the skin;
- Ivermek - intramuscularly;
- Psoroptol is an aerosol.
Treatment procedures and treatment are carried out every 1-2 weeks.
Chorioptosis and its treatment
The causative agents of this type of scabies are small mites, whose body length is up to 0.5 mm. Settling on the body of a cow, they are grouped in certain areas (the root of the tail, the inside of the thighs, the fold of the putty joint), causing itching.
For proper diagnosis, it is necessary to take scraping from a cow in the infected area and send a non-clinical study.
The main symptoms of chorioptosis in cattle are severe itching and the formation of crusts and bald spots on the skin, similar to eczema. Young calves suffer more.
You can get rid of ticks in a cow with the help of "water procedures", that is, bathing in bathtubs where anti-scab drugs are added. Mandatory disinfection of the premises and the destruction of pests is required.
Demodecosis in cows
In the spring-summer season, they are especially active demodexes - ticks that carry a disease called demodecosis. When the air temperature rises to + 30 ° С, they enter the stage of reproduction. Getting on the wool, they make their way to the skin and settle in the sebaceous glands. With strong reproduction, colonies are formed, the number of parasites in which can reach several thousand.
Symptoms of demodicosis are similar to psoroptosis - the formation of skin nodules with fluid, hair loss. The affected areas are located on the head, chest, back and shoulder blades. However, redness is absent, as is itching. The diagnosis is made after laboratory tests of skin scrapings.
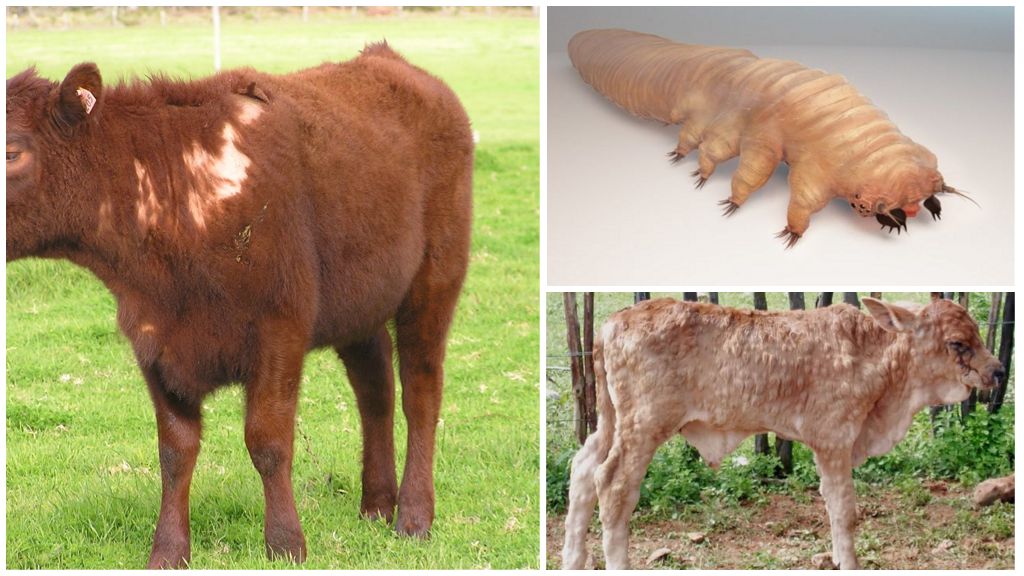
For the treatment of ticks in cattle, medications are used:
- Sevin - solution for spraying damaged skin;
- Ivermectin - injected subcutaneously;
- Acrodex and other aerosols - are used at the initial stage of the disease.
Prevention of ticks in cows
There are 2 types of tick preventive measures for cattle:
- repelling - the use of repellents, including folk recipes;
- exterminating insecticides.
Popular folk remedies:
- coating the cows with a solution of tar and vegetable oil (prepared in a proportion of 1:10) - is done in strips using a bunch of feathers;
- treatment with spent diesel fuel or engine oil - is done in the areas of the armpits, abdomen, lower neck, udder, back, tail and head;
- coating with a solution of shampoo and vegetable oil (prepared in a ratio of 2: 1);
- application for repelling parasites of infusions of odorous herbs (wormwood, tansy, mint, etc.).
Processing should be carried out often during the entire active period of ticks (March-August and September-October), because these funds for action are short-term.
Pharmaceutical preparations for cattle protection:
- Baioflay pur-on - an antiparasitic agent in the form of an oily liquid, is applied by spot application only on clean skin of adult cows weighing more than 300 kg, the duration of protection is 28 days;
- Dust Sevin 7.5% - used to process cows from October to April monthly;
- Centaur, Alezan, etc. - short-acting aerosol preparations;
- Entomozan-S, Chlorophos and others.
All of these drugs help fight ticks in cows, which is necessary for their healthy and active existence, especially in the summer months on grazing. Then they will give tasty and healthy milk, which the owner can use without fear of contracting any infection.