- Tick Life Cycle
- Tick larva
- Tick Disease
Ixodid ticks are one of the most common parasites that inhabit our planet. They are able to live in different climatic conditions, very successfully find the "owner" and transmit rather dangerous infections. Modern science knows more than six hundred species of ixodid ticks. Habitat bloodsuckers covers almost all regions of the Earth, even the Arctic and Antarctic are no exception. On the territory of Russia you can meet representatives of 70 species, the most dangerous and common are dog and taiga ticks, the fight against which is still relevant today.
Morphological signs of ixodid ticks
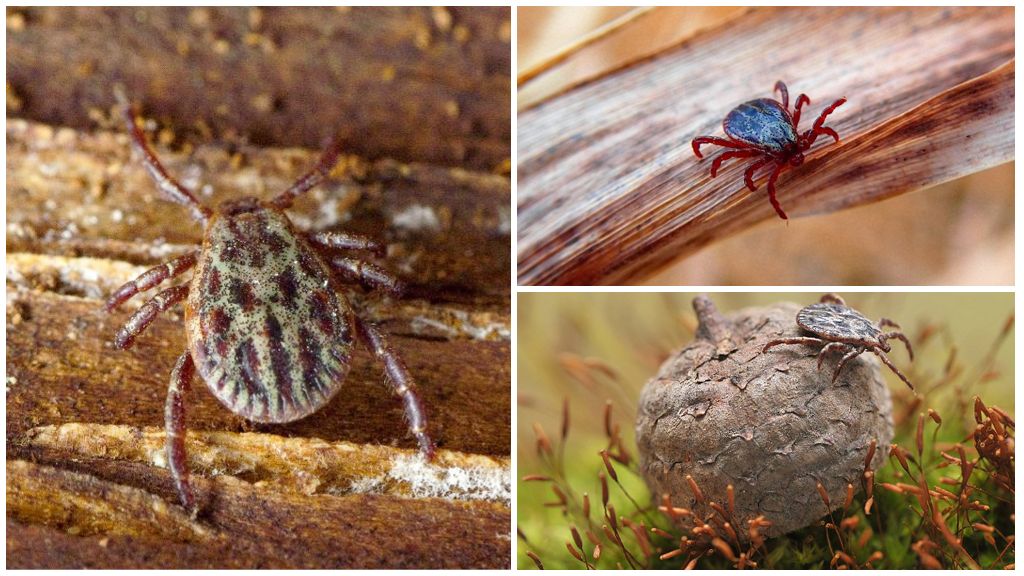
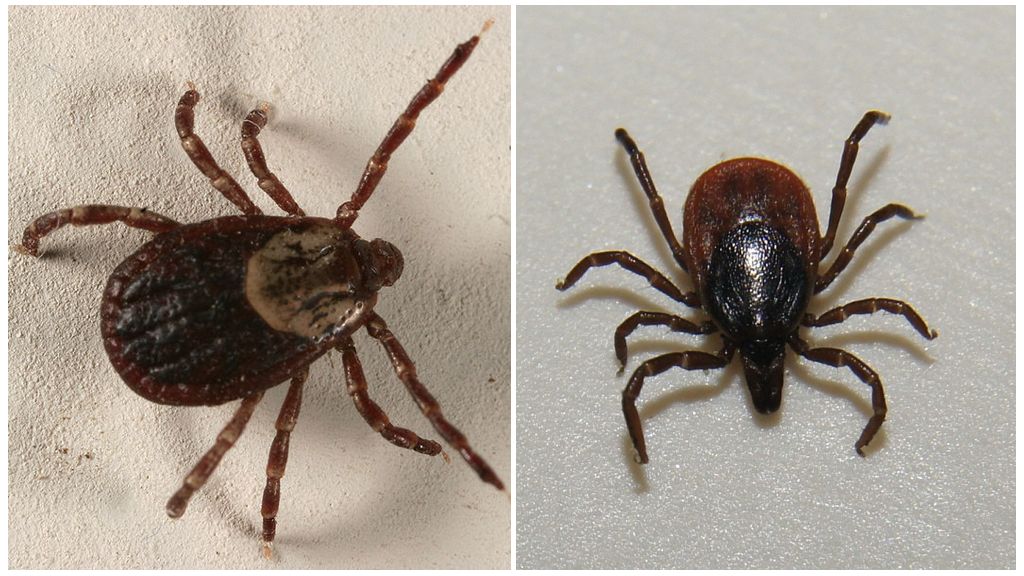
The ixodid tick is a blood-sucking parasite of terrestrial vertebrates (birds, reptiles and mammals), which is part of the tick family of the arachnid order Ixodida. The bloodsucker is a rather large individual: the female grows up to 4 mm, the male - no more than 2.5 mm. A well-fed tick can reach 1 cm. Determine saturated parasite it is possible by color: in the normal state, his body is dark red or brown, after a meal, the parasite acquires a light gray color.
The males on the back have a thickened shiny chitinous formation that covers the whole body, while in the females it covers only the third part. A more clear structure of the arthropod can be seen on the photo of the ixodid tick below.
On a flat oval body are 4 pairs of legs. The tick’s oral apparatus also has its own peculiarities: its proboscis is equipped with a long flat outgrowth with lateral sharp teeth, due to which the parasite is firmly attached to the victim’s tissues, gnaws it and gets to the blood vessel.
On a note!
A puncture wound in the skin of a bloodsucker begins to suck the blood of its owner until it is completely saturated, and the duration of this process can take several days until the pest is detected.
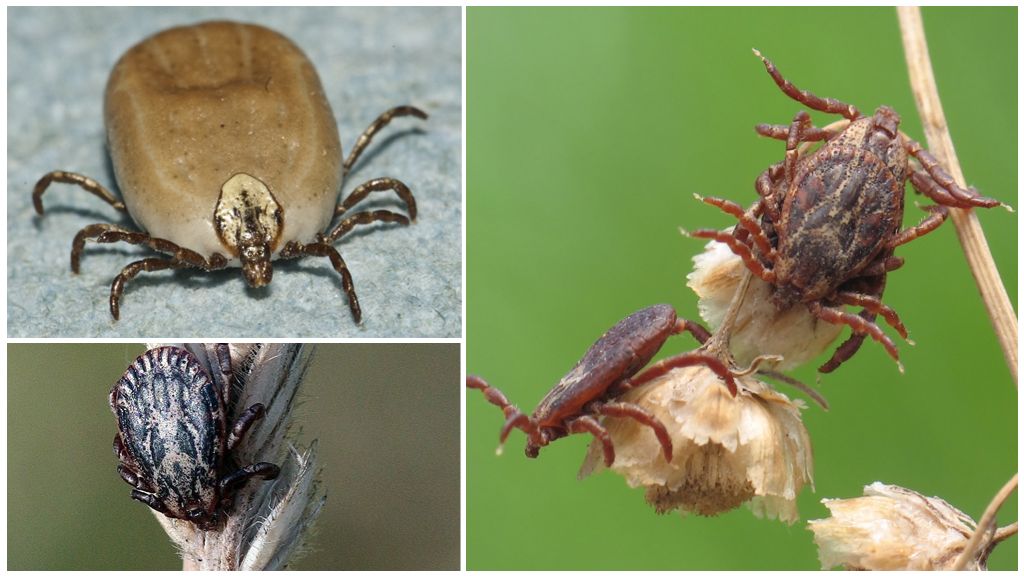
Life cycle
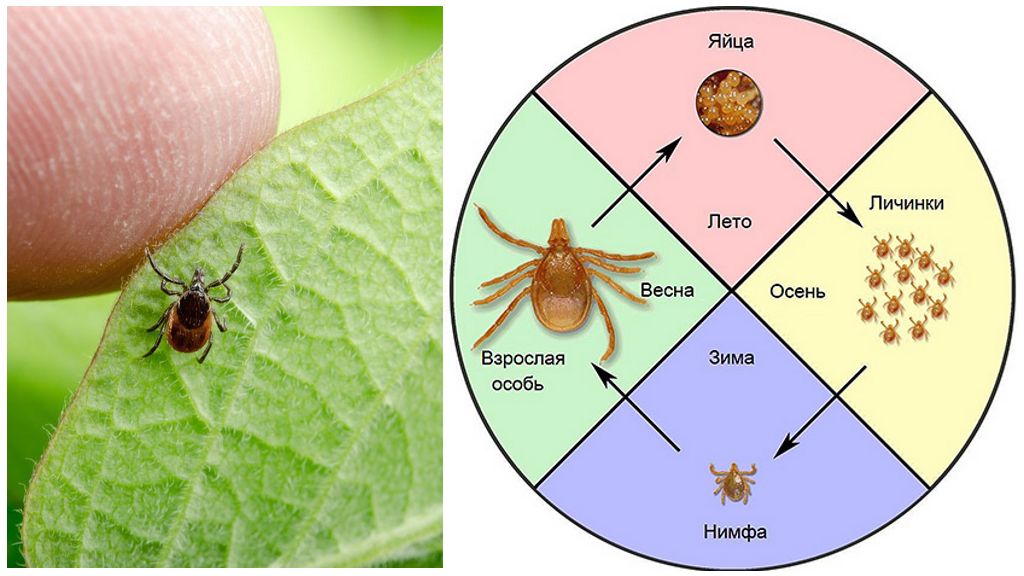
Each tick species has a specific development cycle, the duration of which varies from the habitat of the individual and the availability of food (prey). Average life span ixodid ticks is 1-4 years old.
Ixodid mites usually mate on the body of their victim, in the external environment such a process is extremely rare. Most often, the male approaches the female at the time of her meal; at the end of the process, the male dies.
Saturated with blood and fertilized, the female leaves the body of her victim, setting off in search of a suitable place for laying eggs. Usually, it hides under plant debris or in soil cracks, where within 30-60 days (depending on temperature conditions) it makes eggs laying up to 0.5 mm in size.
On a note!
The number of eggs laid at one time depends not only on the species, but also on the portion of the blood sucked by the individual. Throughout life, one female is able to lay up to 15-17 thousand eggs.
Egg development
The egg development period takes about 2-10 weeks, depending on environmental conditions, in the case of large differences in humidity and air temperature, the future individual dies.The development of embryos slows down when eggs enter the water, it only resumes after removing them from this medium.
Larval development
After some time, the larva of an ixodid tick appears, the dimensions of which do not exceed 1 mm. The development of an individual at this stage can take from 7 to 30 days. A prerequisite for this stage of development is the availability of nutrients, in connection with which, the larva goes in search of its first victim. Most often, it is birds or rodents. Saturated for several days (from 2 to 5 days) with blood, the larva leaves the host body, appearing on the surface of the soil. Then, if there are favorable conditions, she will reincarnate after a month in the stage of the nymph, remaining to winter in this state.
On a note!
The larva is able to live in a state of hunger for two years, but the individual will no longer undergo further development.
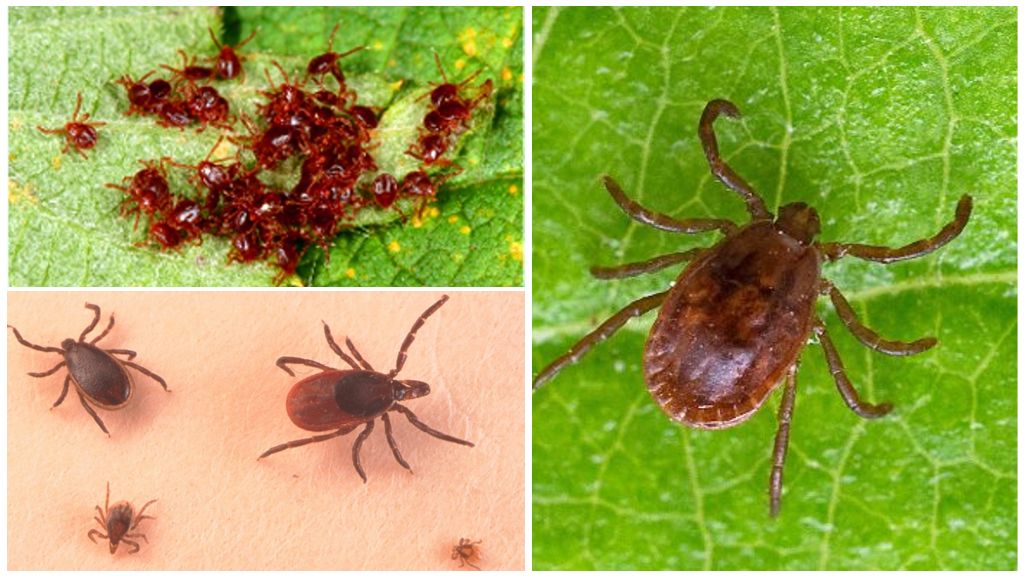

Nymph development
With the arrival of heat, the nymph becomes active, setting off in search of a second host, which can serve not only as a rodent and pet, but also as a person. Outwardly from an adult tick it is distinguished only by more compact body size. The duration of development at this stage takes no more than 5 weeks. Moreover, a significant part of the time (3-8 days) is occupied by the nutrition process: an individual absorbs large volumes of blood, due to which it increases in size and turns into an adult individual (imago). After which sexually mature individuals again breed.
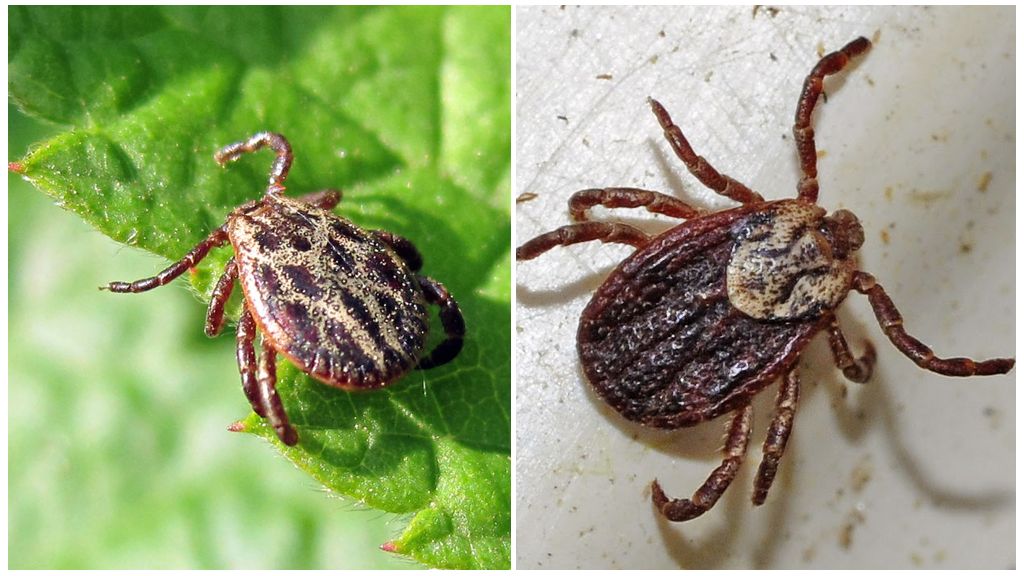
Types of ixodid ticks
Especially dangerous for pets and humans are two types of ticks: canine (Ixodes ricinus) and taiga (Ixodes persulcatus). They are also spread in the territory of the Russian Federation. And if the former live in a wide geographical area, the latter are found throughout the taiga from Primorye to the Urals.
Nymphs and larvae of these parasites feed on small rodents, birds, reptiles. Adult individuals parasitize mainly on large and medium-sized mammals, both wild and domestic. Often ticks stick to a person. Moreover, taiga ticks are especially aggressive.
What is dangerous ixodid tick for humans
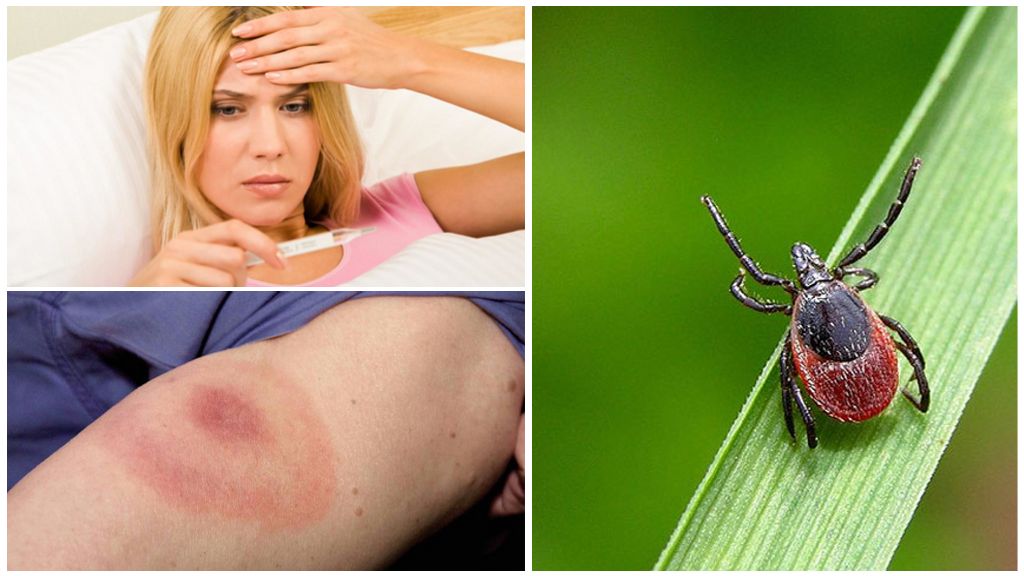

Many species of ticks are carriers tick-borne relapsing fever, ehrlichiosishemorrhagic fevers tularemia and other dangerous infectious diseases. According to doctors, thousands of people become infected with them every year.
For the territory of our country, such infections as:
- Tick-borne encephalitis - a disease caused by a pathogen that penetrates the human body along with the saliva of the parasite. Even if you quickly pull out a tick that was infected with such a virus, a person will still get infected. In a person with encephalitis, the central part of the nervous system is affected, and symptoms of fever appear. A consequence of encephalitis what disability and even death can become.
- Borreliosis or Lyme disease - a disease that is accompanied by various symptoms. In addition to the cardiovascular, nervous and musculoskeletal systems, the respiratory system and the genitourinary system can be affected. The cause of the disease is a special kind of spirochete. In the case of this ailment, the bacterium living in the digestive tract of the parasite is excreted from its body during nutrition and enters the victim’s blood stream. Usually this happens after 2-3 hours from the moment of the bite. Therefore, if timely notice and extract ixodid tickthen infection can be completely prevented.
Important!
However, it is sometimes quite difficult to separate the sucking tick from the owner, in such situations you should immediately seek medical help, since the consequences of the introduction of the parasite into the human body can be irreversible.
Knowing how many parasites live, how quickly they multiply, and what consequences may have tick bites, when entering the forest it is necessary to use not only the right equipment, but also special Remedies. Only timely control measures will help prevent a bloodsucker attack and avoid negative consequences.






