- Dog tick
- Dog tick breeding cycle
- Tick-borne diseases
The nickname for a dog tick in the Russian-speaking space is tightly fixed for one of the species of the ixodidae family with the Latin name Ixodes ricinus. The name is not entirely true, since this parasite is a polyphage that can feed on so many species of mammals, including humans. In Europe, it is also called cattle and European wood tick.
On a note!
Can also parasitize on dogs sarcoptoid and demodectic mites. Demodectic more deserves the name of a dog tick, as it is a highly specialized parasite and infects only canids.
Appearance of an ixodid tick
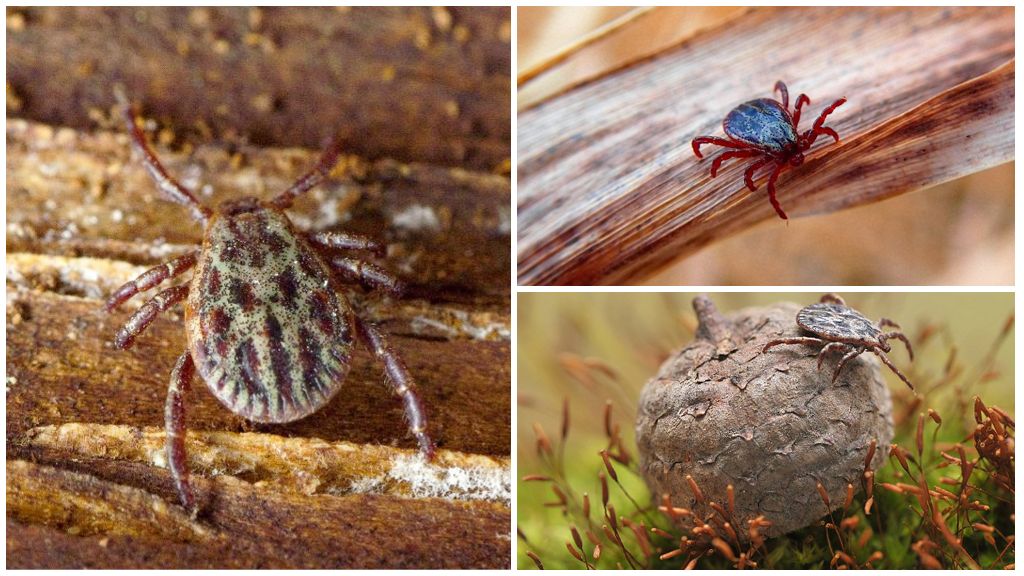
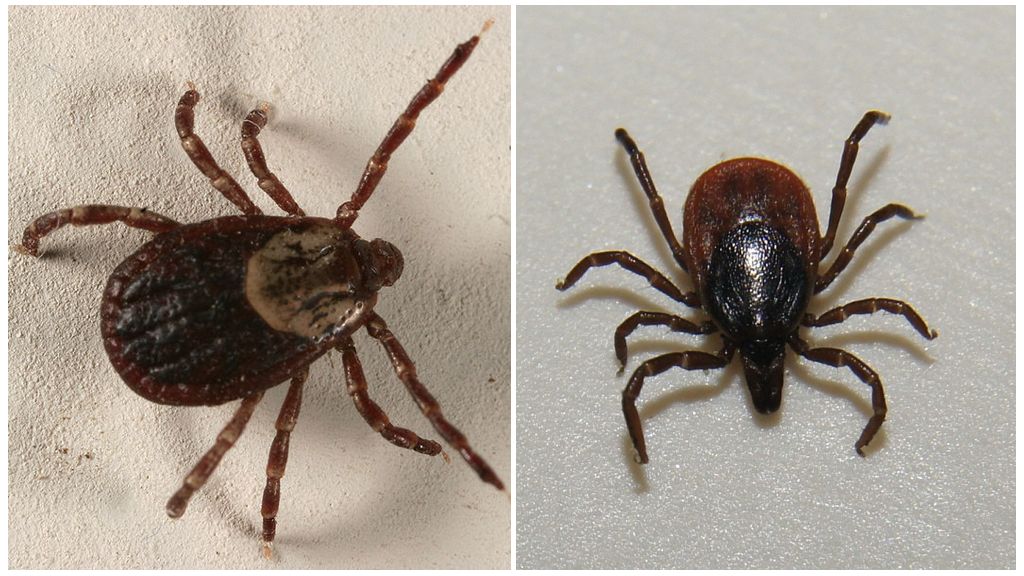
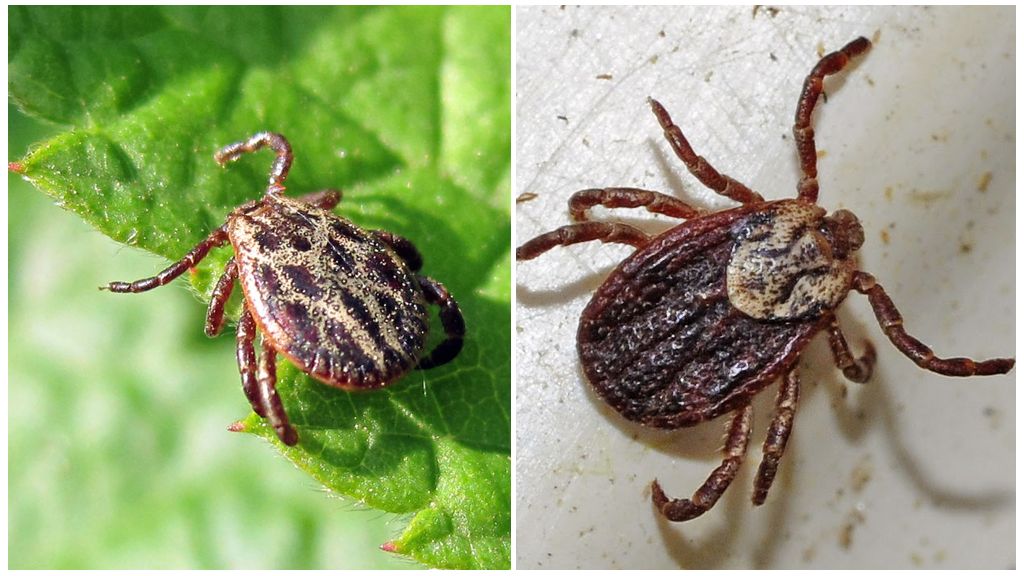
Dog - arthropod, belonging to the group of "hard" ticks. Crush it is easy, but not required. They are called solid because of the shell that almost completely covers the male's egg-shaped body. The hungry female also gives the impression of being completely protected by this shell. After feeding, the female’s body swells and the real shield becomes almost invisible, since it covers only the chest of the ixod. The external and internal structure of the dog tick is the same as that of others ixodic.
On a note!
These arthropods do not have full eyes. Adult males up to 3 mm in size, hungry adult females up to 3.5 mm. After eating the size the body of the female can reach 11 mm.
The color of the male dog tick is brown, the color of half-decayed foliage. The hungry female has a similar color, but a light gray stripe is visible on the sides of the abdomen. After feeding, the female becomes like a ball of light gray color with a small dark dot on the front end of the trunk and brown legs that do not reach the ground.
Habitat
A dog tick is distributed throughout the central and southern parts of Eurasia. It is also found in North Africa and North America. In the latter, with a high degree of probability, the parasite was introduced. The area of the dog tick reaches in the north to Iceland. But in the northern regions it is replaced taiga tick. In Central Russia, these two species coexist on the same territory.

According to scientists, distribution area this arthropod is limited by external factors. Several mild winters in Scandinavia led to the spread of the parasite north of the normal border.
The habitat of the dog tick is relatively humid. But the main factor that attracts the parasite is animals for food. There are more mammals in forests, forest-steppes and meadows than in the arid region. But drought to the dog tick is not an obstacle. In the absence of other living conditions, he feels great even in hot and dry regions.
On a note!
Ticks are relatively cold-resistant creatures. Them activity begins in March, when there is still snow on the ground.
Life cycle
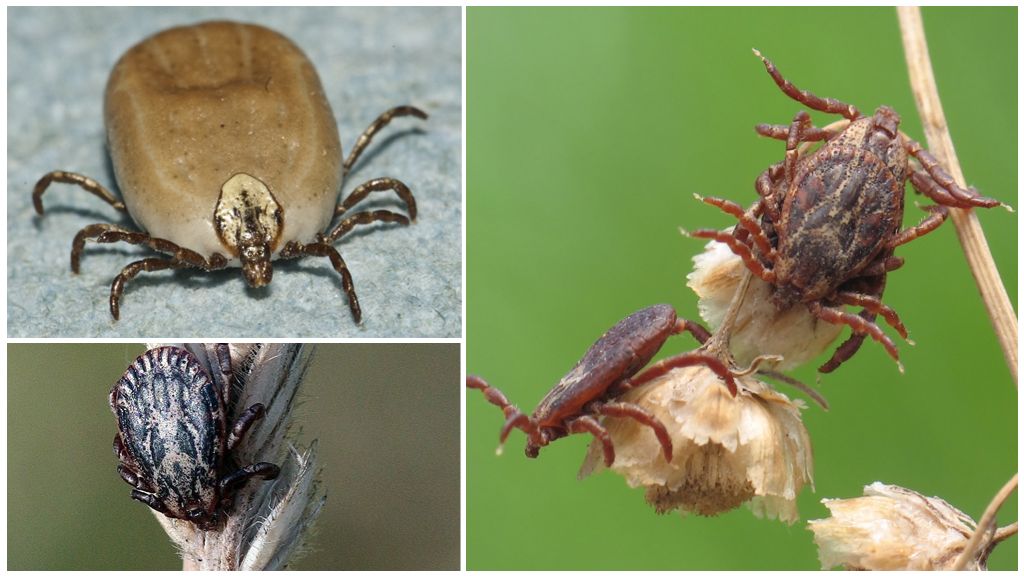
A dog tick is a three-host polyphage. General development cycle takes 2-3 years. Under very favorable conditions, arthropod develops very quickly and passes the whole life path in a year. In very adverse conditions, development is delayed up to 6 years.
After the pumped, fertilized female fell to the ground and laid eggs, the appeared larvae are not very active in searching for the host. Basically, they are limited to insects and shrews, although their menu also includes:
- reptiles;
- the bats;
- rodents;
- birds;
- rabbits.
The larvae of canine ixodid ticks are almost never found in dogs. These are the owners of the second and third stages of development. Larvae drink blood 3-5 days. After that they fall to the ground and molt into a nymph.
The nymph is more active. Having got out of the old skin, she rises on the grass to hunt small and medium mammals, which include dogs. The nymph’s lifestyle is the same as that of the adult, but at this stage the parasite cannot yet multiply. The most active nymphs during morning and evening dew. They are sensitive to dehydration and are forced to descend closer to moist soil on a hot afternoon.
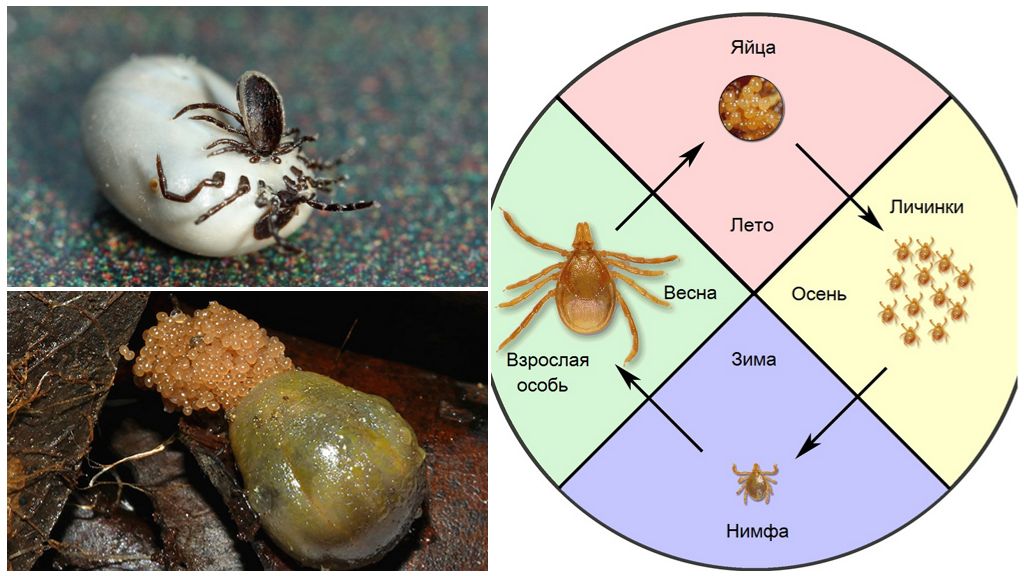
After eating for the second time, the nymph sheds into an adult, sexually mature individual. Adults feed on large mammals:
- cattle;
- sheep
- goats
- horses
- deer;
- by people.
In humans, a dog tick is almost not found due to the fact that it creeps on the body for too long, choosing a place for food. But if the victim for a long time did not pay attention to the arthropod, it can also suck. Females drink blood for 6-13 days before falling off and laying eggs.
The female is unlikely to succeed in multiplying by eating on humans. There are 2 reasons for this:
- too long a period of nutrition, it will be noticed and removed before it falls off itself;
- a male must be paired, which sucks next to the female.
On a note!
But if it fails to breed, then the female will be able to transmit the virus that she “grabbed” from a sick animal. That's why tick control starts in early spring.
Disease carriers
A dog tick, like any other type of ixodidae, can tolerate a large number of diseases. Some pathogens are safe for humans, but can cause the death of pets:
- Luping's disease;
- pasture fever.
Other diseases in humans and animals are common:
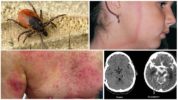
- borreliosis;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- Q fever;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
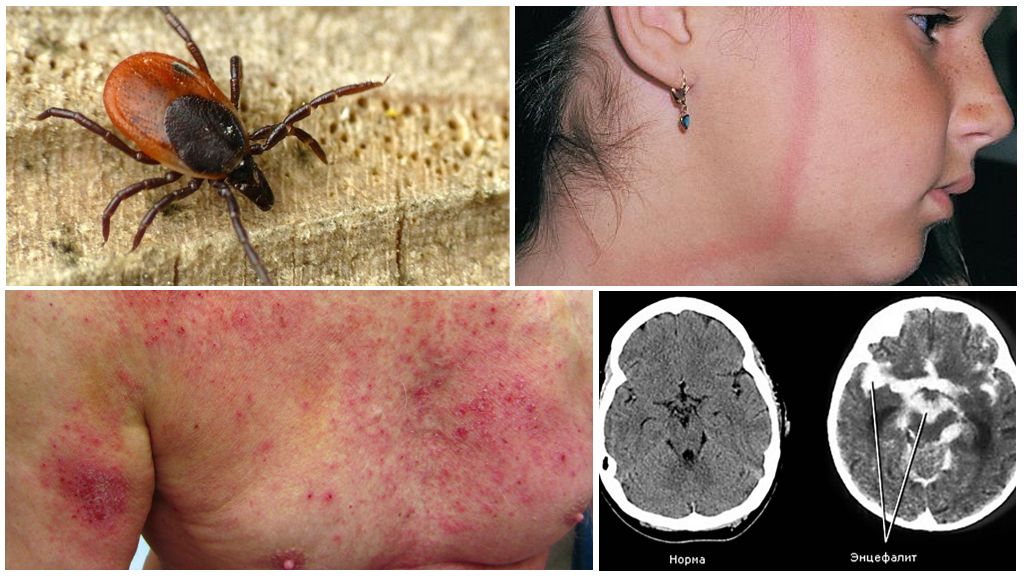
If ticks bit people as often as animals, we would all be sick with Staphylococcus aureus. 30% of humanity are carriers of this disease. In Russia, only ticks infected with tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis have medical value. Both diseases are dangerous and relatively widespread in the Russian Federation.
Important!
Live parasites removed from humans deliver to the laboratory for research. Delivery time is one day.
How to deal with ticks in dogs
Ways to deal with ixodic dog ticks have long been worked out. To repel parasites:
To kill a sucked arthropod:
- chewable tablets;
- drops;
- injections.
Ixodes are large parasites and it is not very difficult to notice that a dog needs help. But sometimes bald spots form in the animal due to hair loss. Not very attentive owners attribute this to the appeared whipworms.
Vlasoed - a highly specialized insect. Each owner has its own type of beetle. On dogs it is not found at all. If the animal is treated with an anthelmintic and tick-borne preparation, then there is no place for the lizard to come from. These drugs act on it the same way as on fleas.
Bald spots may appear due to activation of well protected from external influences demodex subcutaneous tick. Like the human tick of this group, canine demodex is constantly present on the animal. While the dog has strong immunity, parasites do not manifest themselves. Activation of demodexes indicates a weakening of the protective mechanisms of the animal.