- Types of forest ticks
- Tick development cycle
- Red beetles
- Tick Remedies
Forest tick (Ixodes ricinus) in the Russian-speaking tradition is better known as a dog. These are the same arthropods that animals bring home in clusters after walking in nature and in parks. These arachnids belong to the ixodidae family - the most dangerous parasites for humans. Forest - an erroneous name that combines at least 3 morphologically similar species. For this reason, photos of the forest tick in different sources may differ from each other.
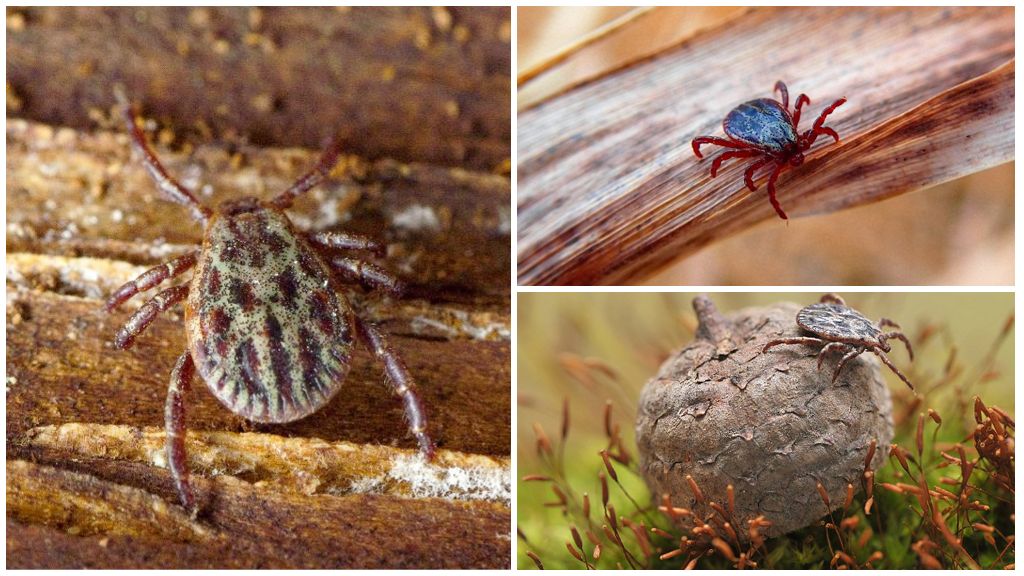
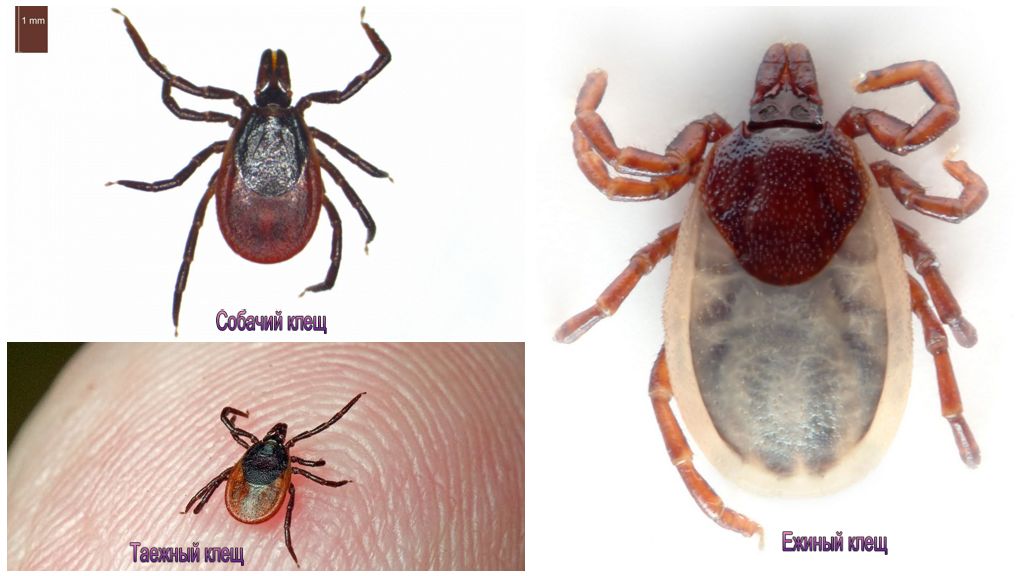
Types of forest ticks
In the forests of Eurasia, the most common 3 species of ixodidae:
All three species live in the same biotopes and their ranges overlap. Since these species look similar to the eyes of a layman, like two drops of water, in everyday life they are combined under the general name “forest tick”. But there are some differences: the main owner of the hedge tick is the European common hedgehog, and the canine in Europe is called cattle because of parasitization on livestock.
On a note!
Due to the very wide distribution of Ixodes ricinus (canine), it is also called the European forest tick.

Areas
It is wrong to call a dog tick European, since its range completely captures the entire Eurasian continent plus North Africa and North America. He obviously came to America with immigrants. In southern Eurasia, this arachnid completely crowds out its counterpart: the taiga tick.
The main part of the range of the taiga tick is in the southern and middle zones of the taiga. In the west, the borders of the range reach the north of Western Europe.
The tick is common in the east of Western Europe and in Siberia. The bulk of this species lives in the Siberian part of Eurasia.
Morphology
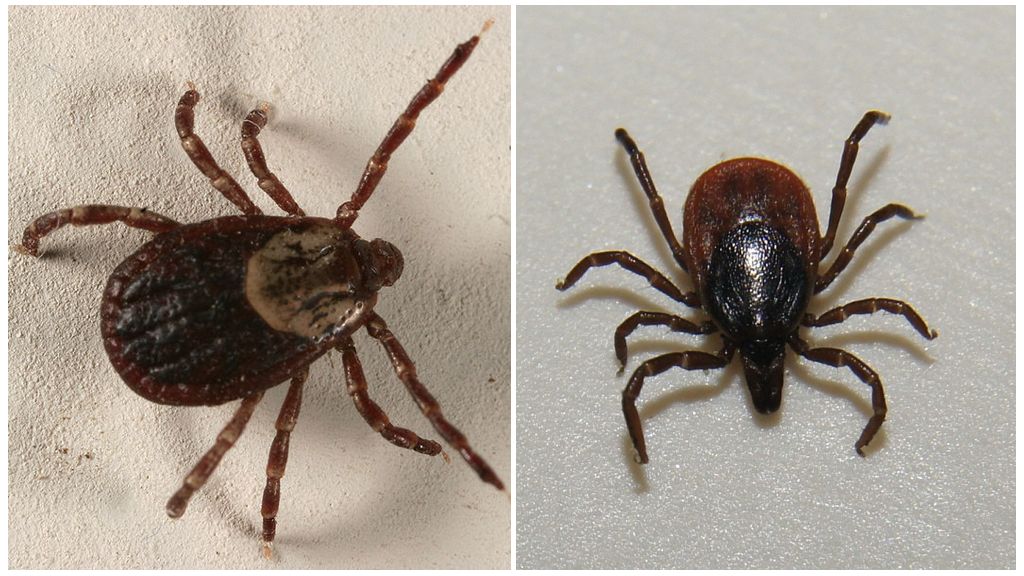
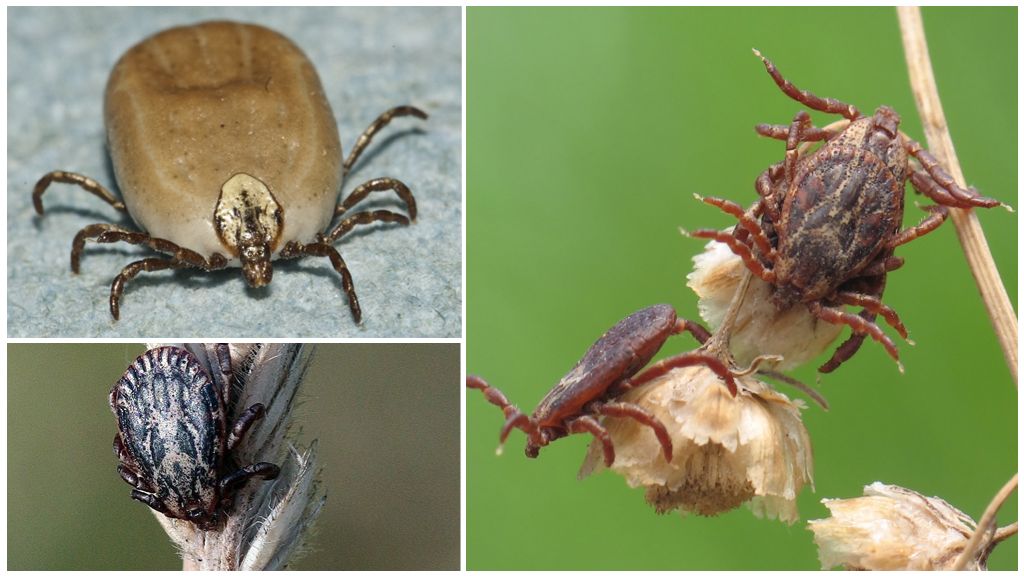
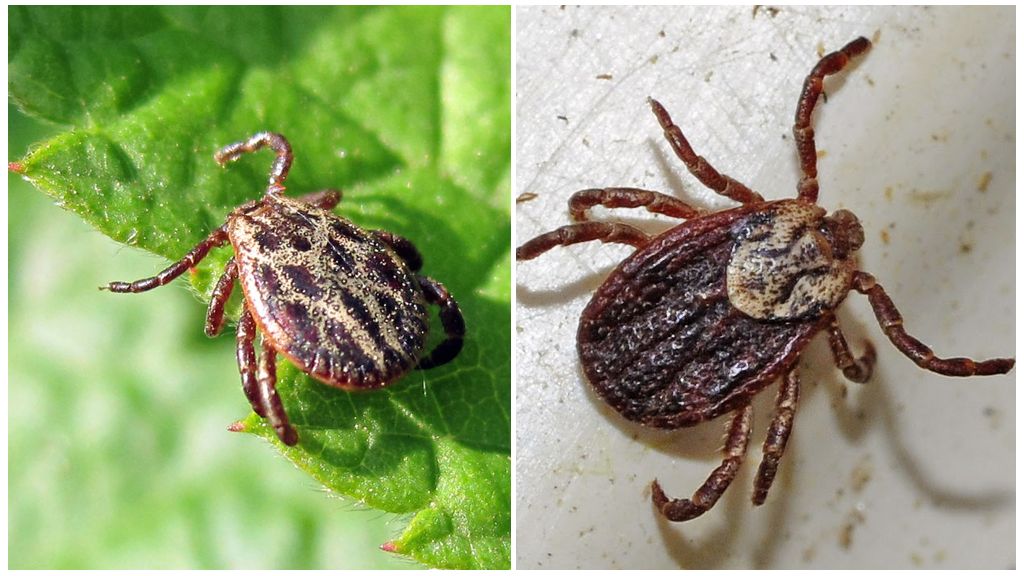
All 3 species of forest ticks have a flat egg-shaped body. The length of a hungry female is up to 4 mm, and that of a male is 2.5 mm. The sucking female increases in sizes up to 1 cm. For this reason, the body of a female is poorly protected by a rigid shield that almost completely covers the back of the male. All forest ticks have a brown color. The only difference in the hedgehog: a bent first pair of paws. In two other species, the first pair of legs is straight.
On a note!
If the tick is up to 1.5 mm in size - this is a nymph.
Lifestyle
Ticks live in the forests, but you can also meet them in the meadow and in the city park. Multiply forest ticks are mainly on the host. Over the summer, the female lays up to 17 thousand eggs. Fertility depends on the amount of blood consumed. Due to developmental difficulties, only a few survive to adulthood.
How many ticks live depends on the climate. Full development cycle may take from 1 year to 7 years. In cold climates, development slows down. Also, the vital activity of parasites depends on environmental conditions. In warm regions, forest ticks are also active in winter. The minimum temperature threshold at which arachnid begins to develop is 9 ° C.
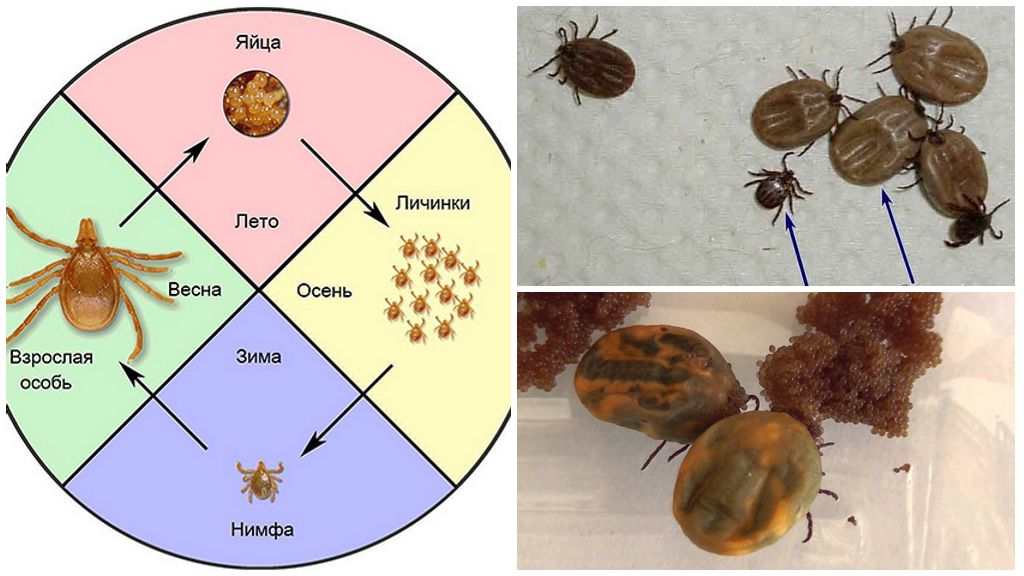
On a note!
Forest ticks have three developmental phases: larva, nymph and adult animal. Outwardly, they are similar, but young individuals have fewer paws. To go to the next stage of development, the tick must be fed with blood.
A forest tick is dangerous due to this developmental feature.After drinking blood, the larva / nymph falls away from the host and molt already on the ground. If one of them drinks the blood of a sick animal and next time attacks a person, then the victim will receive one of the diseases:
- tularemia;
- Lyme disease;
- encephalitis;
- Marseilles fever.
All three species are polyphages, that is, they are able to feed on different types of warm-blooded organisms.
There are other ticks that pose a danger to humans: reddish or grassy. Ixodic and reddish mites equally await the victim on the stalks of grass. Because of this ixodic often also called herbal. But in real herbal ticks, only larvae lead a parasitic lifestyle.
Red beetles
Very small species of parasites. Adult individuals about 1 mm in size, larvae - 0.02 mm. Parasitic larvae in mice cause thrombidiasis in humans. Signs of thrombidiasis:
- itchy sore spots;
- nodules;
- pustules.
The symptoms are very similar to flea bites.
On a note!
Since clothes prevent the larvae from spreading freely throughout the body, the main area of damage in humans is the ankles.
When bitten, larvae can transmit some infectious diseases:
- Q fever;
- Tsutsugamushi
- African tick-borne rickettsiosis.
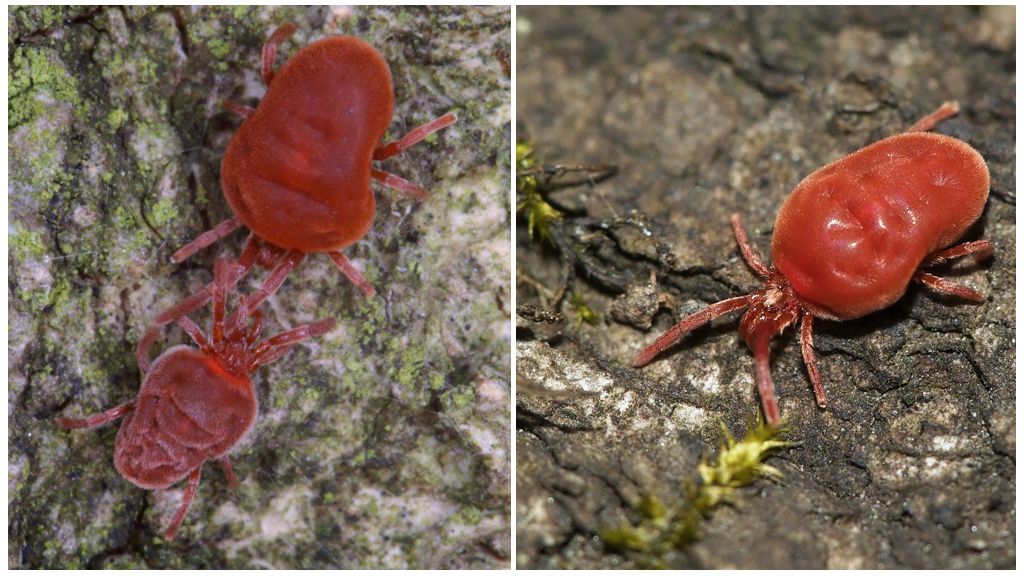

Thrombidiasis is caused by the larvae themselves. It is not blood that serves them as food, as for ixodids, but skin cells. Larvae inhabit red-tick mites under the skin, in the hair follicles. The body reacts to the introduction of the larva by the formation of irritated spots and itching. When combing, there may be a complication - pyoderma. The latter is caused by pyogenic cocci. After feeding for several days, the larvae fall away from the host and the remaining stages of transformation take place on the ground.
Control measures
The meeting with the reds is a rare occurrence. With ixodic people encounters much more often. Tick protection The ixodic family has been worked out in vivo for a long time. The basis of this protection is special clothing that does not allow arthropods to reach the body. Also apply modern repellents:
- Diethyltoluamide. The drug can be applied to the body and clothes. The duration of action, depending on the concentration of the drug in the insect repellent, is 2-3 hours. Diethyltoluamide only repels arachnids, since they do not like smell. Because of this, the substance does not act in a strong wind.
- Permethrin. It can be used not only as an insecticide, but also as an acaricide. Affects the nervous system of parasites. Apply to clothes. Validity 2 weeks, if not washed.
- Ikaridin. A relatively new drug that paralyzes arachnids.
- Alphacipermetrin. Acaricidalkilling parasites. Apply only to clothing. Valid 2 weeks or until first wash. Prevents suction of ixod.
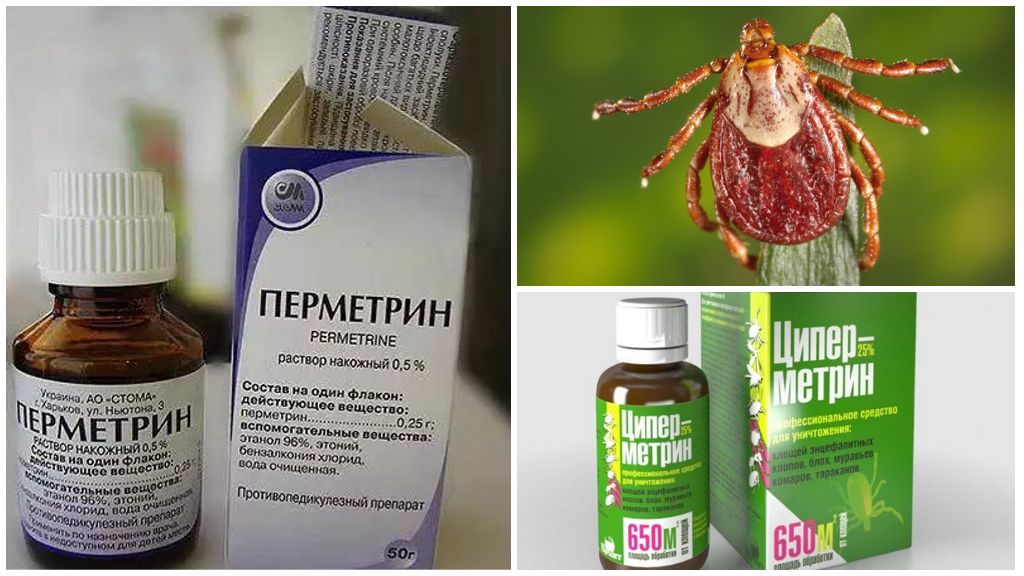
Important!
Buying a more expensive product containing several toxic substances does not make sense. This is the manufacturer’s marketing move. The duration of such a tool will be determined by the most long-acting substance.
Forest Ixodes in the apartment
Previously, the state took care of forest ticks. It so effectively fought against the forest tick by spraying acaricidal products over the forests that the population did not even imagine the true size of the population of this arachnid. After the collapse of the USSR extermination of parasites ceased and arthropods are experiencing an outbreak of numbers. They began to appear even in apartments.
And the answer to the question, where do forest ticks come from in the city dwelling, is very simple: they “come” from the parks on animals or people. After stopping the fight against parasites in the parks from the wild, they migrated with birds and wild mammals.
Nobody wants to live in an apartment breathing poisonous chemistry. Therefore, in housing it is more advisable to use folk remedies that scare away these unpleasant creatures. Like insects arachnids are afraid aromatic herbs and essential oils. But this is a weak defense and it is better to use it against fleas.
On a note!
Inquisitive experimenters found that wood ash does not kill ticks. Therefore, this folk remedy against arachnids is useless. It is unpleasant for them, but not dangerous.
The best option for combating ticks in an apartment is to provide animals with protection against bloodsuckers and check their clothes themselves after forest walks. Traditional barriers of repelling substances on the windowsill, the threshold of the apartment and in the ventilation in this case do not work.







