- Mite taiga
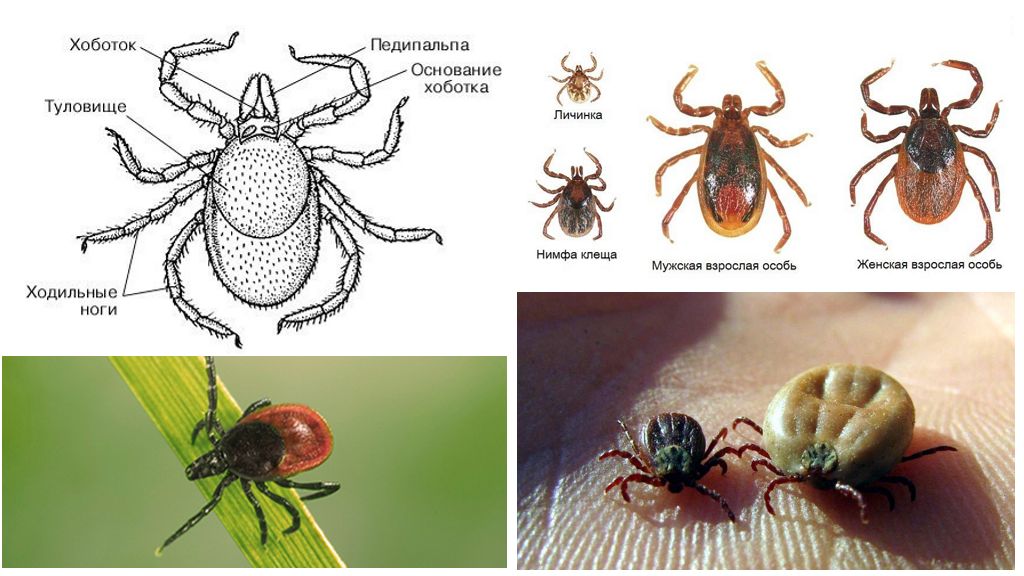
- Tick body structure
- Tick Nutrition
- Ticks: dermacenter and ixodid
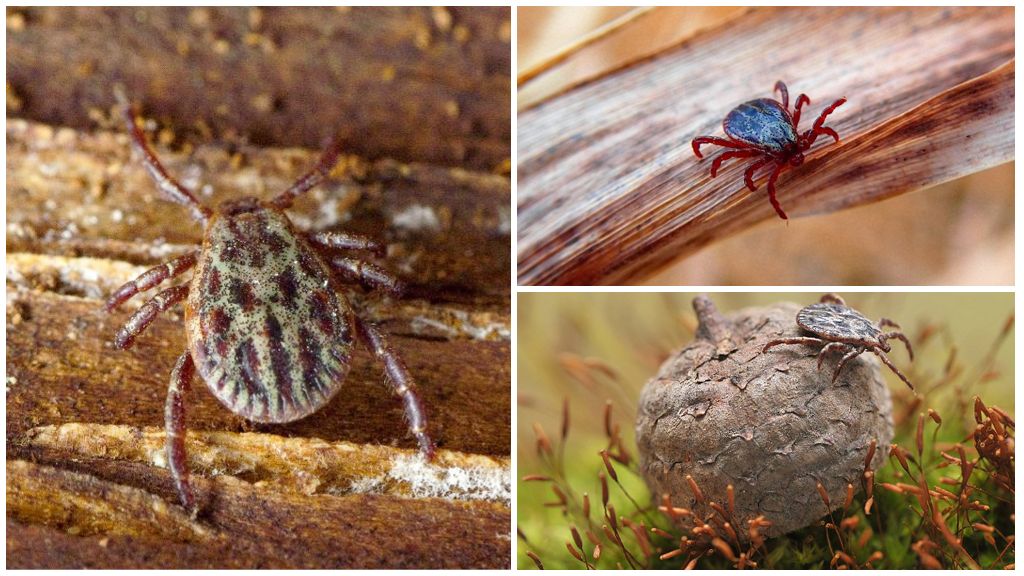
The taiga tick (Ixodes persulcatus) is one of the representatives of the ixodidae family, wearing a hard shell. It is a carrier of eastern type of encephalitis. But this is due to the presence on the territory of its habitat of animals that are resistant to the virus and have it in the blood. On a “clean” territory, a taiga tick is dangerous no more than any other type of these parasites. Blood-sucking arthropods tolerate a sufficient number of other types of diseases.
Area of taiga tick
This is one of the most northern. types of ticks. In terms of frost resistance, taiga is superior only to Dermacentor reticulatus, it is also meadow, wood tick. In the southern regions: Krasnodar Territory, Crimea, Stavropol Territory - taiga replaces the dog "brother". In the central zone of Russia canine and taiga ticks coexist in the same territory. Only taiga and meadow parasites.
The taiga tick is widespread in the middle and southern subzones of the taiga. In Russia, the border of its range passes north of Ulyanovsk and Samara regions. This representative of arachnids is found in Belarus and the Baltic states. In the north it captures part of Western Europe, the southern regions of Finland and Karelia, Moscow and Leningrad region. In the east, the range is torn:
- the main part along the Lena and Ob rivers, as well as to the north;
- in the Far East to the south of Primorye and northeast of China;
- focal areas: in the mountain ranges of Central Asia, Japan, Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands and Kamchatka.
On a note!
But the data is somewhat outdated. From unpleasant news: due to warming, the taiga tick appeared in large quantities where it had not existed before. In Finland, the species expanded its range to the north and cases of taiga encephalitis have already been reported.
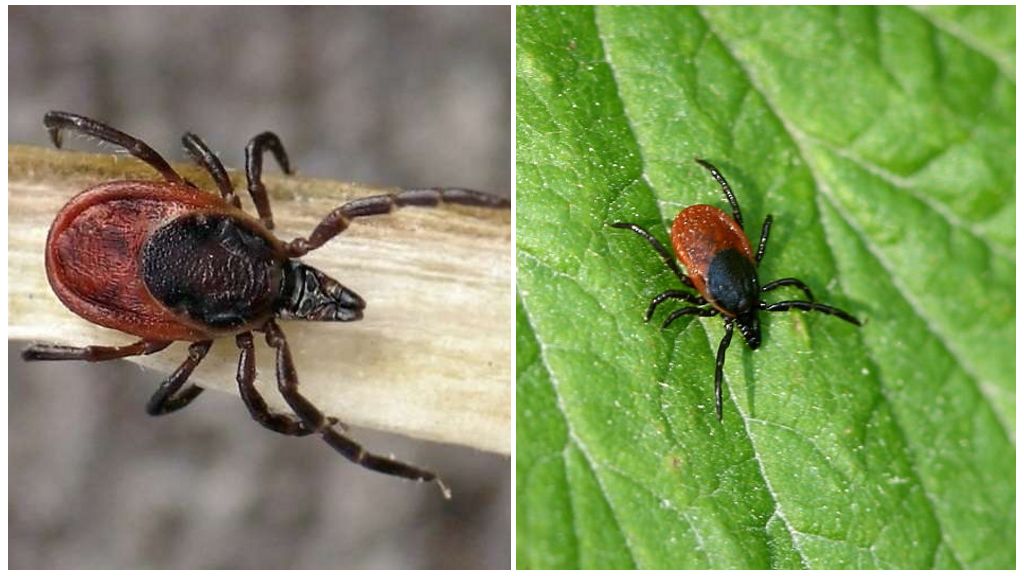

The taiga tick prefers damp terrain, therefore its main habitat is mixed forests, taiga, individual groves in the middle of meadows, spruce forests. But it can also come across in water meadows and forest edges. In this regard, the forest tick is very similar to taiga. In regions where their ranges intersect, they can occur in the same territory.
Appearance
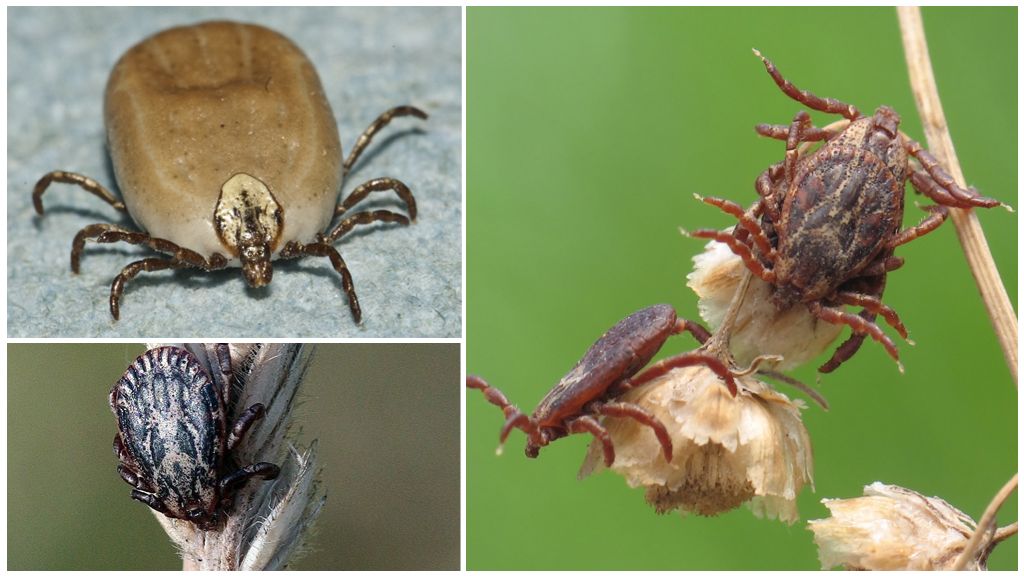
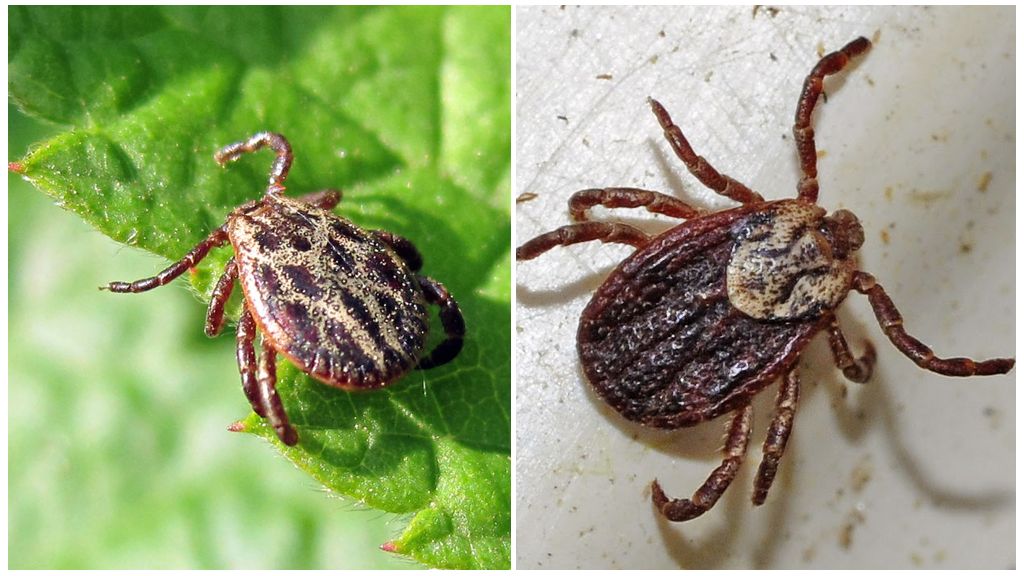
The body length of a hungry female is 3-4 mm, the male is 2-3 mm. A well-fed female increases in sizes up to 13 mm. The structure of the taiga tick and other ixodes of this genus are the same. Externally, they can be distinguished by color when carefully examined. Other differences are visible only under a microscope. Sometimes the difference in color without a microscope is also poorly noticeable. The black-footed tick (in Latin Ixodes scapularis) almost repeats the coloring of the taiga. Even in the photo of a taiga tick it is difficult to distinguish from a black-footed one, if the images are not nearby.
On a note!
The main differences: the front pair of paws and range. The black-legged forepaws are bent inward at rest. Have taiga straightened. The Blackfoot habitat is North America. In Eurasia, it can be met only with random introductions.
The rest is morphology and biology of all ticks of the genus Ixodes same.
Body structure
The body is egg-shaped with fused breasts. The head is very small. On it are organs that feel heat. In taiga ticks, sexual dimorphism is well developed.It is expressed in the difference in the size of the guards and mouthparts. The female and male have a hard shield protecting the parasite from above. But in the male, a dark-brown shield covers almost the entire body. In the female, the shield covers only the breast, leaving the red abdomen free. With the oral apparatus, the opposite is true: in the male it is reduced, in the female it is well developed.
On a note!
Due to the fact that the abdomen of a female is not protected, it has the ability to increase several times during feeding.
The oral apparatus is a piercing-sucking type. The salivary glands containing anesthetic saliva and encephalitis virus enter the mouth. The oral apparatus passes into the throat. This is followed by the esophagus and intestines. The intestine consists of 3 sections:
- middle intestine;
- fine;
- back.
The middle intestine has several lateral blind branches that are filled with blood during nutrition. The hind gut ends with the anus.
Near the hind legs are air-conducting trachea. The circulatory system of the tick is not developed and the lymph is poured into the body cavity, where it is saturated with oxygen due to trachea.
Life cycle
The genus of Ixodes has 4 stages of development:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph;
- imago.
Life span Ixodes persulcatus is dependent on environmental conditions. The warmer the climate, the faster the transformation. In the conditions of the Leningrad region, a full development cycle takes 3 years. A year for each blood-sucking stage. The development of the larva and nymph in favorable conditions takes 11-12 months. The imago lives 11 months.
On a note!
Sexual dimorphism in nymphs and taiga tick larvae is expressed in a difference in size. And you need to calculate gender based on statistics.
At the pre-maginal stages, ticks that emerged from eggs in August can eat before or after winter, but their transformation begins and ends at the same time as those born in the earlier months (from late June to early August). Metamorphosis lasts 1-2 months. Survival in a hungry state in larvae and nymphs is high: 88-100%.
Nutrition
Taiga tick - polyphage with a wide forage base. Larvae and nymphs attack small mammals and birds.
On a note!
A nymph can stick to a person, although this happens very rarely.
Adult ticks feed on the blood of ungulates and carnivores. Since this species has recently come across cities, parasites can also attack dogs and cats. Man also falls into the realm of imago interests. The nature of the nutrition of the taiga tick provides for a triple change of hosts, because of which the parasite becomes a carrier of human diseases.
At the last stage, the female feeds mainly. It is able to stick to the host for a long time and absorb large portions of blood. The male either does not drink blood at all, or sucks for a very short time. Immature stages are all blood-sucking.
This species usually does not rise above 1 m. The taiga ticks lie in wait near the paths for 1-4 weeks. Noticing the approach of the future owner, the bloodsucker throws forward the first two pairs of paws and clings to the coat. Or clothes if it's a person. Having moved to the victim, the parasite finds a convenient place and sticks.
On a note!
Ixodid ticks can determine the appearance of a victim for several hundred meters.
The similarity and difference of ixods and dermacenters
The difference between the two groups of ixodides is of interest to the arachnid biologist. In the taxonomy of ticks, both genera belong to the same family. The classification of the family has not yet been established and exists in two versions:
- Philippova classification of 1997;
- modern classification from 2013.
According to the latter, the family has 6 subfamilies. Ixodidae: taiga and dog, - belong to the subfamily Ixodinae; dermacenters: grazing, meadow / forest, - to the subfamily Rhipicephalinae.
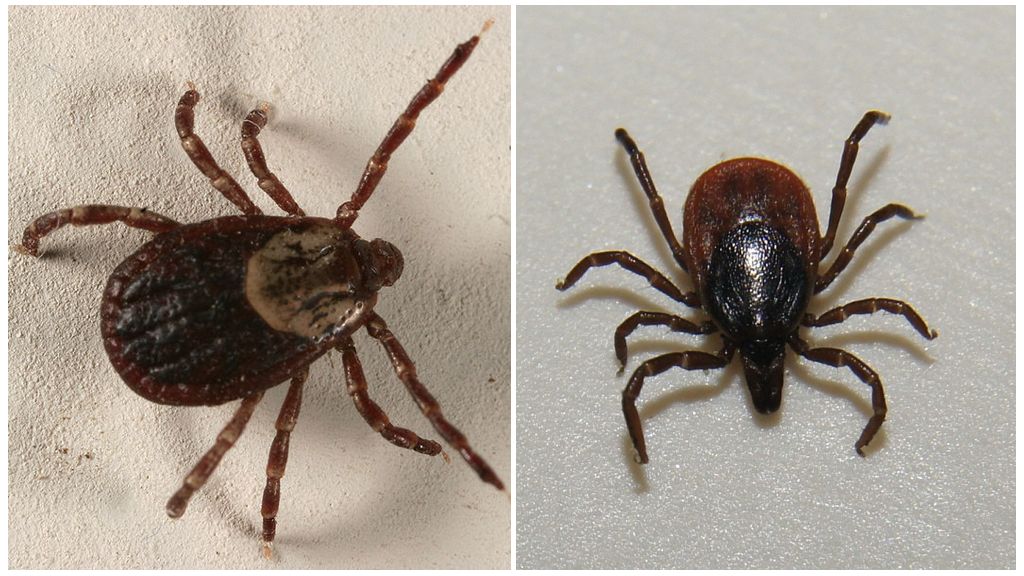
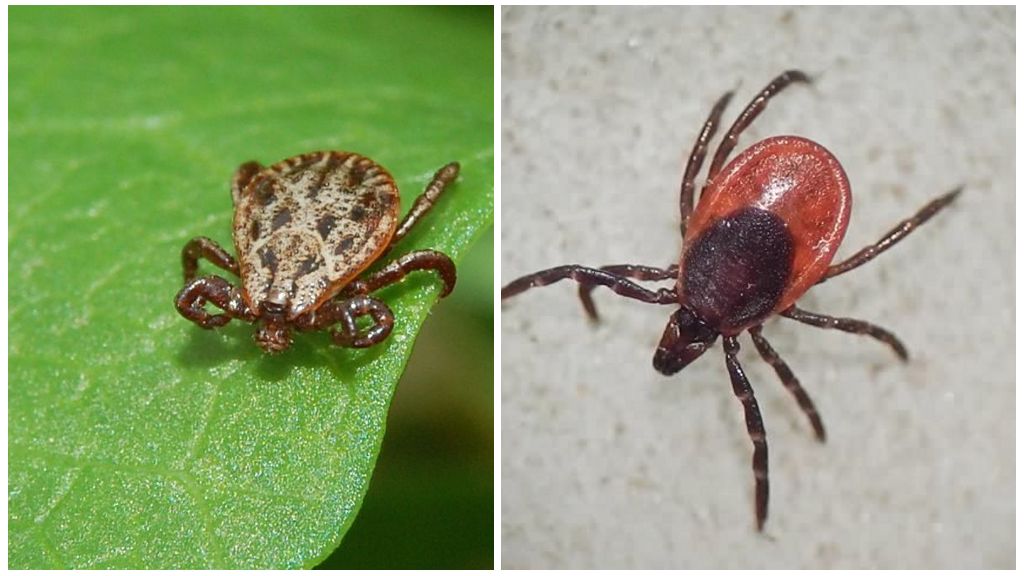
Taiga from a dog is distinguished by a brighter red-brown color. The canine male is dark brown.In a female dog, a gray stripe is visible around the abdomen. When saturated, the female of this species becomes light gray.
On a note!
Dermacenters differ from ixodic bright coloring. They are not in vain called "patterned" ticks. The shell of the male is covered with a light pattern. The female has a pattern only on the shield covering her breasts.

Other differences are less obvious:
- dermacenters can climb to a height of 1.5 m, ixodic only up to 1 m;
- in the development of dermacenters there are 2 blood-sucking stages, in the development of ixodic - three;
- dermacenters are more resistant to acaricidal drugs than ixodic drugs;
- Dermacenters can cover longer distances by hunting the victim.
Observations must be made to see these differences. People affected by tick bite, anyway, at what height the parasite was and how far it crawled.
Tick Danger
From the point of view of doctors and visitors of the forest zone, the similarity between the different species of this family is much more important:
- during life parasitize on several hosts;
- carry a number of microorganisms dangerous to humans, including the causative agent of encephalitis.
The most dangerous bite of a taiga tick for a person in an area that is a natural reservoir tick-borne encephalitis. But even in a safe area, ticks can infect unpleasant diseases, among which borreliosis. Even in areas of poor encephalitis, only 6% of ticks are carriers of the virus. But borreliosis already carries 20% of the total population.
What to do with a bite
If, after returning from a walk, a sucking parasite was found on the body, it is carefully removed, placed in a jar and carried to analysis.
Important!
Only a living arthropod has medical significance.
For this reason, even a bloodsucker cannot be killed. It must be delivered to the laboratory within the first day. As prevention of encephalitis in the same 24 hours do an injection immunoglobulin.