- Encephalitis Mites
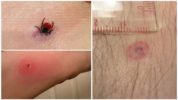
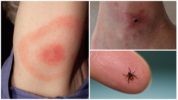
- Encephalitis tick bite on a human body
- Encephalitis Tick Bite
- Tick-borne encephalitis symptoms
- Types of Tick-borne Encephalitis
- Tick-borne encephalitis treatment
With the onset of warm summer days, many tend to spend time outside the noisy city - in the forest or by the river. When gathering with family and friends for a picnic, do not neglect the dangers posed by ticks. Observance of precautionary measures, constant inspection of clothes, bodies will allow timely detection of the parasite. These tiny representatives of the fauna are carriers of a dangerous insidious disease called tick-borne encephalitis.
Important!
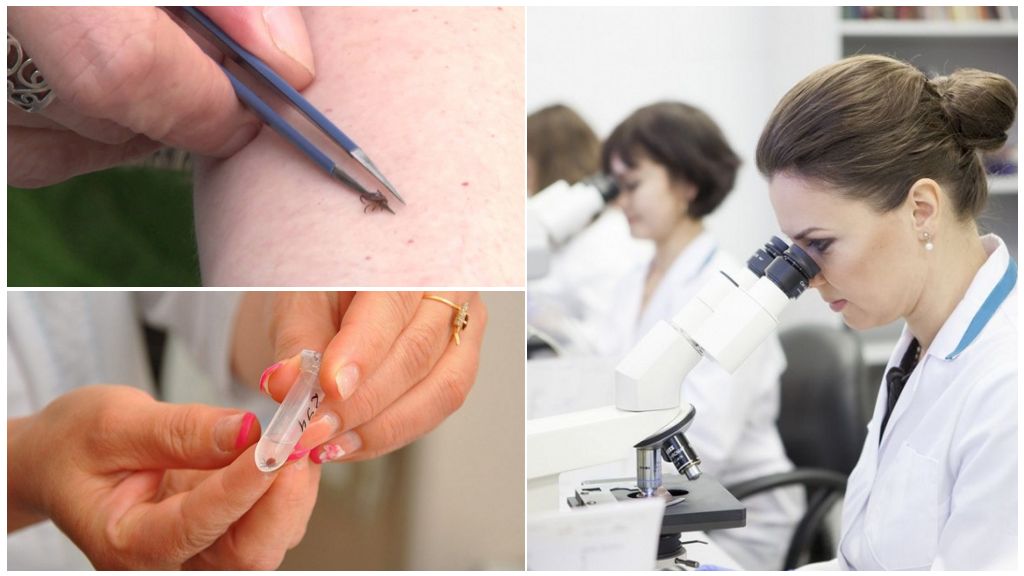
It is impossible to distinguish a visually infected tick from encephalitis from a sterile parasite. To establish the degree of danger from a bite will allow a clinical laboratory study, which can be carried out in Moscow or another village.
Let us consider in more detail what the disease is, as well as the symptoms and treatment of tick-borne encephalitis.
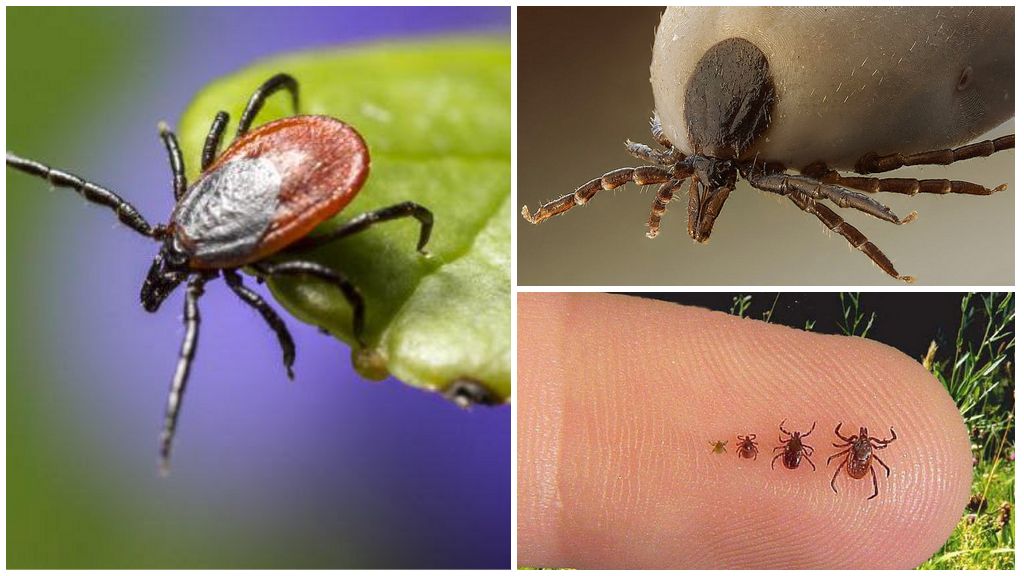
Ticks
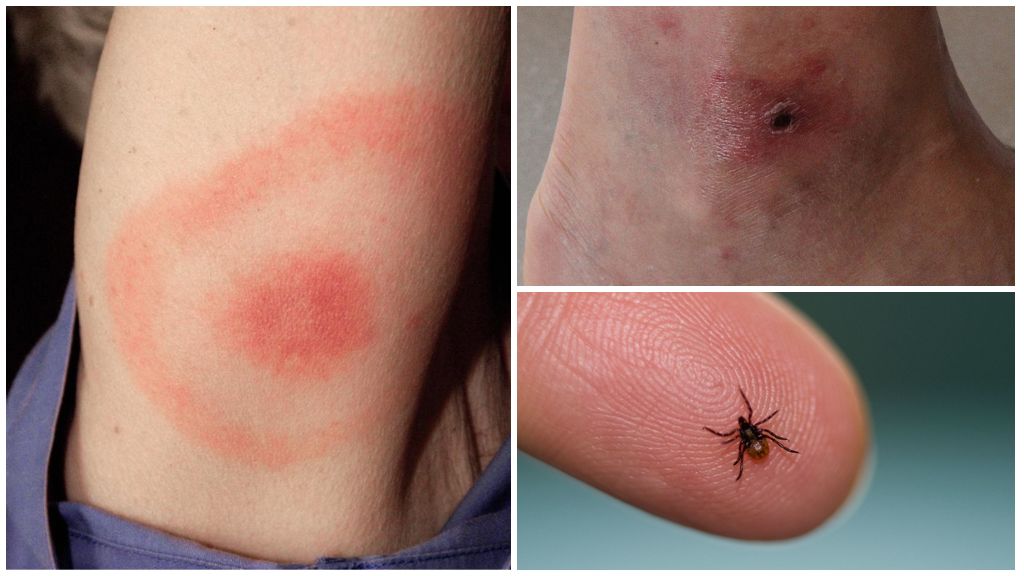
These creatures look like insects, but they do not belong to them. Ticks, spiders and scorpions stand out in a separate class of arthropods - the family of arachnids. The main difference between arachnids is the number of legs, which they have 4 pairs. Encephalitis tick in length reaches no more than 3-4 mm.
On a note!
Parasite activity begins in early April, and by mid-May reaches peak levels. By this time, their number is increasing millions of times and the epidemiological threshold of incidence sharply goes up.
With the onset of the mating season (mid-May), females ixodid ticksHaving drunk blood, they begin to lay eggs. After a month, larvae appear from them, which immediately begin to bite, infecting their victims with a dangerous virus. Period activity of an adult encephalitis tick is approximately 3-4 months. Some representatives of the parasites can be found in late October. The ixodids belong to about 650 species of ticks. In Russia, tick-borne encephalitis virus spreads by two types of arthropods - taiga and canine by individuals. They parasitize not only on domestic animals - goats, sheep, cows, dogs, as well as other mammals that become carriers of a dangerous viral infection.
In nature encephalitis ticks inhabit at a distance of not more than 0.5 meters from the ground. They choose an object by smell, since they do not have organs of vision. Cling to clothes or human skin very tightly with the help of special hooks located on the legs. Encephalitis ticks fall extremely rarely on top of their prey.

On a note!
After blood saturation of the victim, the body of the tick increases significantly sizes and can reach 3 cm.
The science of epidemiology classifies tick-borne encephalitis as a natural focal disease that occurs in certain areas, with a humid climate favorable for animal life and an abundance of animals for food.The main habitat of the encephalitis tick is Siberia, the Urals, the Far East, China and Mongolia. However, outbreaks are often recorded in forest regions of Eastern Europe and Scandinavia.
What is dangerous encephalitis tick
Quite often as a result tick bite a person develops encephalitis - inflammation of the brain, the etiology of which is different. By attacking the central nervous system, the virus can lead to paralysis, mental disorders, or even death. In places of bites in people, swelling and a limited area of inflammation can appear. Encephalitis mite meticulously seeks out a place where you can dig into the skin. Bloodsucker bite is dangerous by the fact that he:
- absolutely painless;
- several individuals can stick to a person at once;
- most often, the parasite is found on the body only after a few days, when it significantly increased in size, pumping blood.
Remove the sticky tick quite difficult, therefore, this procedure is recommended to be carried out in a clinic or in another medical institution. Favorite places on the human body are such areas:
- axillary and popliteal hollows;
- groin;
- neck and area behind the ears;
- scalp;
- lower back;
- folds on the stomach.
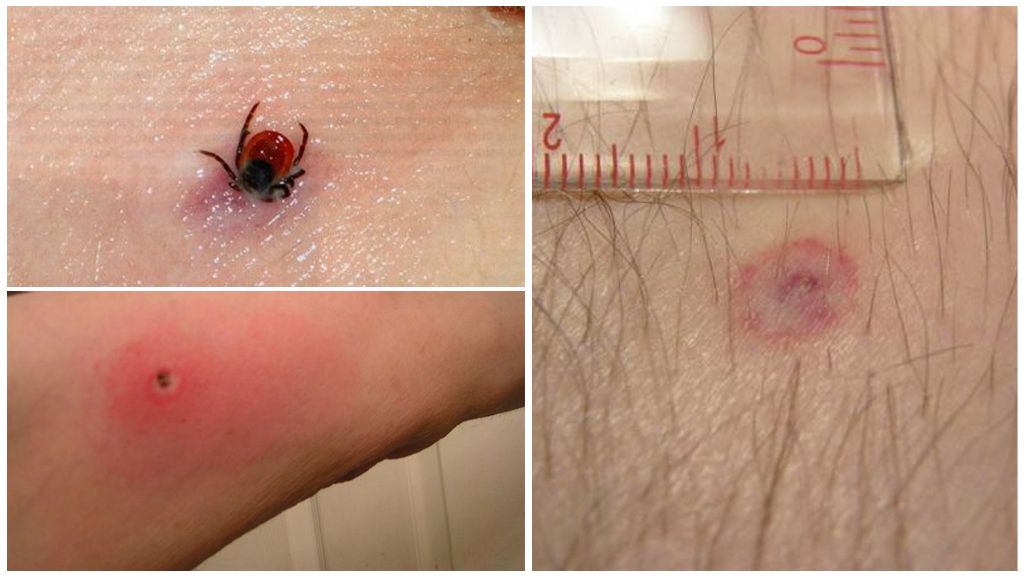
These sites have a thin skin and are rich in blood vessels. At the suction point of the arthropod, a focus of inflammation develops, which is accompanied by soreness and redness, as can be seen in the photo of the bite of an encephalitis tick on the human body.
Important!
The body's response to the presence of a virus in it depends on the state of the human immune system, as well as on the proximity of the parasite attachment to the brain.
After the encephalitis tick has reliably settled on the skin, the infection with blood flow quickly spreads and reaches the brain. The severity of the course of the disease and its form depend on the amount of virus in the body, the number of bites, the geographic location of the parasite. The most severe forms of the disease are recorded after an attack of taiga encephalitis ticks. Fatal outcome occurs in 20-40% of cases, as evidenced by statistical data.
Bite emergency
First aid for detecting a sucking tick on the human body is to remove the parasite. All manipulations must be done carefully so as not to tear off the proboscis, which is deep in the skin. Their sequence can be represented as follows:
- As close to the surface of the skin as possible, grab the parasite with tweezers, a loop of thread, special device or just with fingers wrapped in a bandage.
- Turning the body of the tick counterclockwise, carefully moving it upward from the wound.
- Treat the bite site with any disinfectant.
- Wash hands thoroughly.
The recovered parasite must be placed in a well-closing container and send for research to the laboratory. If it was not possible to remove the bloodsucker, then you must immediately contact the nearest medical institution.
What is tick-borne encephalitis - the causes of the disease
Dangerous viral disease tick-borne encephalitis has its own code for ICD 10 - A84. It refers to the so-called vector-borne infections that are transmitted to humans through the blood-sucking ixodic representatives of the fauna. The causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis is arbovirus from the genus of flaviviruses (Flavivirus). By its size, a particle in the form of a ball with small protrusions on the surface is 2 times smaller than the influenza virus and 3-4 times smaller than measles. This allows her to easily overcome all the protective barriers of the immune system.
Dangerous arbovirus exhibits poor resistance to UV radiation, disinfectants, high temperatures, does not live long without its owner.When boiling, it dies within a few minutes, but at low temperature indicators, the virus is able to maintain its vital activity. The main source of infection is an encephalitis tick that attacks not only humans, but also mammals that live near humans or in the wild. Thus, a vicious circle is formed along which the virus circulates: tick - animal - tick.
There are two main ways of transmitting the disease: transmissible - through the bite of a parasite and alimentary, that is, the fecal-oral method. Thus, we can name the main causes of tick-borne viral encephalitis. These include the following factors:
- bite of an infected arachnid;
- ingestion of feces of an ixodid tick on human skin and after combing, the penetration of infection into the blood;
- accidental crushing of the parasite when trying to extract.
You can become infected with encephalitis without a tick bite and get sick through milk and dairy products that have not undergone appropriate heat treatment and were obtained from infected animals.
The action of the virus in the human body
Tick-borne viral encephalitis, the causative agent of which is localized in the digestive system, genital and salivary glands of ixodic parasites, has a devastating effect on the central nervous system and the human brain. The pathogenesis of a dangerous disease can be described as follows:
- overcoming the first obstacle to the internal organs, which include the skin or digestive system;
- the formation of macrophages - special blood cells for disinfecting the virus, but they become the breeding ground of the infection;
- concentration of infection in the lymph nodes;
- penetration into internal organs and central nervous system with blood flow;
- damage to the gray matter, nerve endings, shell of the brain and spinal cord.
In the acute course of the disease, one can observe a slow recovery of the affected tissues, the development of stable immunity. A thorough examination of the patient indicates that changes in the body occur not only at the level of nerve cells, but also in the respiratory system, stomach and intestines.
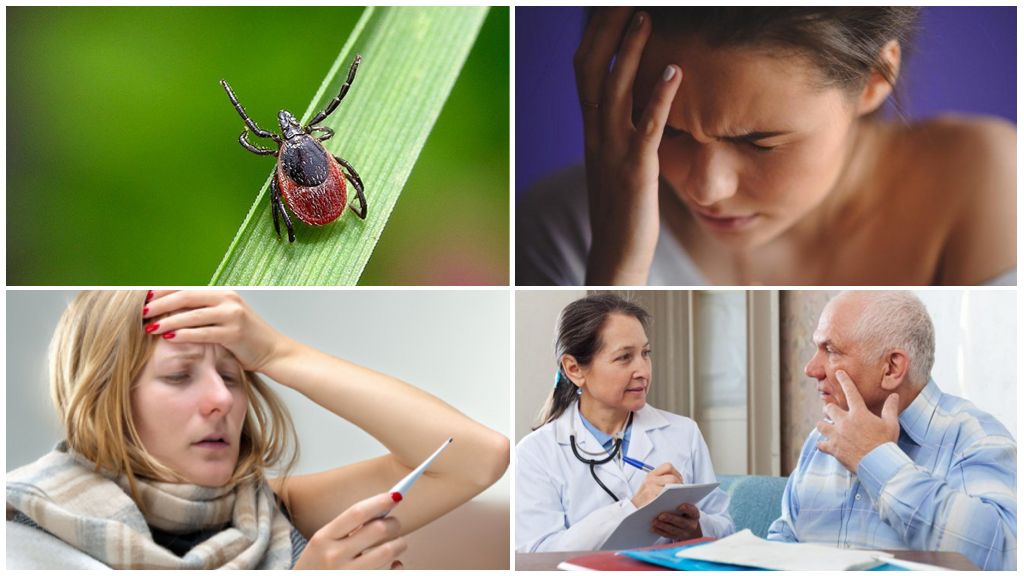
How tick-borne encephalitis manifests itself
Signs of encephalitis after a tick bite occur approximately 2-3 weeks after infection in the human body. Usually incubation period lasts from 7 to 20 days, depending on the method of infection. With weak immunity, infectious disease specialists record fulminant forms of the disease, the first symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis appear almost a day later. With a protracted type, the incubation period can last 30 or more days without showing any signs of the disease.
On a note!
A person infected with tick-borne encephalitis is not dangerous to others.
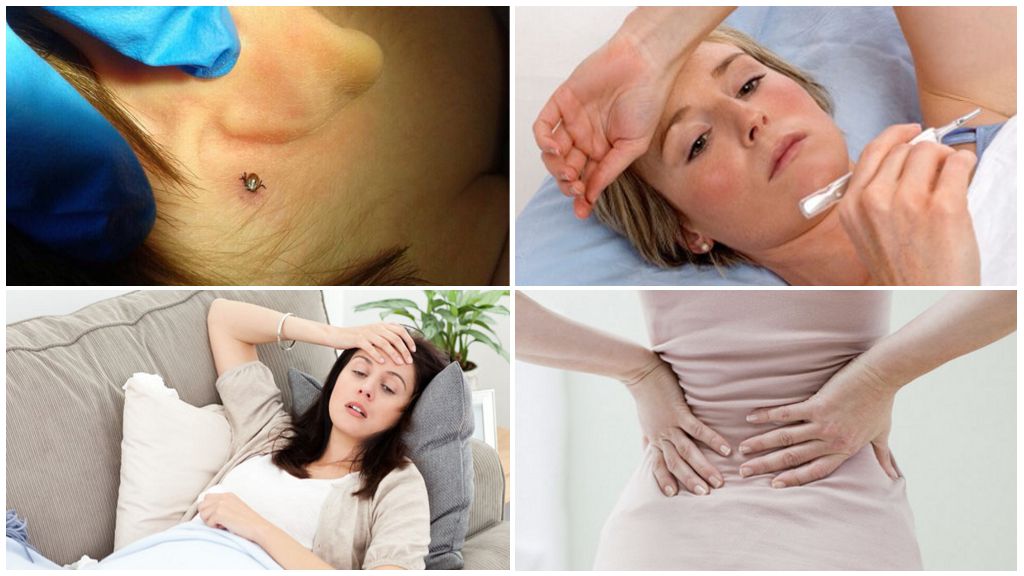
The course of the disease is conditionally divided into several periods. The initial phase is characterized by the absence of a clinical picture. The main danger is that you can lose time and tick-borne encephalitis will develop in full force. The first symptoms after a tick bite are almost identical and resemble in their specificity a common cold disease with the following characteristic features:
- an increase in body temperature to 39-40 degrees with characteristic chills and fever;
- strong pain in the lower back and limbs;
- general weakness, nausea, and vomiting;
- pain in the eyes;
- lethargy, lethargy, drowsiness;
- the patient’s consciousness remains.
Identified first signs of a dangerous disease require immediate treatment in a medical institution. The correct diagnosis and treatment technique is established by infectious disease specialists. With a thorough examination, a specialist can detect specific changes in the patient’s condition:
- redness of the face, skin of the body and neck;
- low blood pressure and heart rate;
- white coating on the tongue;
- rapid breathing and dyspnea at rest.
When the digestive tract is affected, bloating and constipation appear. Starting from 3-4 days, the disease can go into the phase of neurotic changes. Tick-borne encephalitis virus enters the membrane and substance of the brain, causing symptoms such as:
- multiple cramps;
- double vision
- muscle tingling and crawling sensation;
- weakening of the movements of the limbs and their partial numbness;
- later, disorders in the activity of the cardiovascular and digestive systems may occur.
The consequences of an encephalitis tick bite can appear in such options:
- recovery with a gradual long recovery;
- the transition of the disease into a chronic form;
- fatal outcome.
Important!
In order to prevent an irreparable situation and many serious complications, a person should find an ixodid tick on his body as soon as possible to go to the hospital for help.
Variety of types and forms
Depending on the subtype of the parasite, these types of tick-borne encephalitis are distinguished:
- Far Eastern. It is characterized by an acute course of the disease, starting with a fever. Subsequent symptoms are manifested rapidly, leading to paralysis and coma. After about a week, the patient may die. The carrier of the infection is a Siberian or taiga encephalitis tick.
- European. It has two phases of development. The first manifests itself as flu and lasts for 7 days. The second is characterized by damage to the nervous system of varying severity - from mild meningitis to encephalitis. Fatal outcome is observed in 2-3% of cases. The carrier is a dog ixodid tick.

A more detailed classification of diseases is developed on the basis of prevailing general infectious, membranous and focal symptoms of central nervous system damage. In medical practice, such forms of tick-borne encephalitis are thoroughly studied and described in detail:
- The febrile form proceeds as a common catarrhal disease with no signs of central nervous system damage. An increase in temperature is observed during the week, and then an independent recovery occurs. Symptoms - general weakness, excessive sweating, cardiac arrhythmia.
- Meningeal form is one of the most common. The signs of inflammation of the brain and spinal cord are clearly expressed. Against the background of elevated temperature, meningeal symptoms appear - vomiting, overstrain of the muscles of the occipital part of the head, neck, pain, motor agitation, hallucinations are observed. The form ends with a full recovery in 2-3 weeks, leaving for a long time increased fatigue, sleep disturbance, emotional disturbances, poor physical exercise tolerance.
- Meningoencephalitic. It is characterized by a two-wave temperature reaction, each of which lasts on average from 2 to 7 days. The interval between the waves is 1-2 weeks. The first stage is characterized by general toxic symptoms, and the second has meningeal and cerebral symptoms. The prognosis for this form is favorable, it is possible to cure the patient without complications.
- Polio form. It is characterized by damage to the cells of the spinal cord. During the first days, the patient feels weak, quickly tired. Then problems begin with facial expressions, arms, legs, numbness of certain areas of the skin develops. An infected person cannot keep his head in a natural position, make controlled movements with arms and legs, suffers from severe pain. Muscles can significantly decrease in volume. Full recovery is not possible, paralysis and atrophic paresis remain.
- Polyradiculoneuritis. It is observed extremely rarely.In addition to the symptoms of meningitis, a sensitivity disorder in the central parts of the body is diagnosed. The disease is characterized by pain in the affected nerves and paralysis.
- The polyencephalitic form develops very rapidly. The first symptoms of an encephalitis tick bite appear 3-4 days after infection. The nerves of the jaw and larynx are affected, speech impairment is observed, swallowing and chewing reflexes are difficult, asymmetry of the face develops, respiratory failure is provoked.
- The polyencephalomyelitis form is characterized by simultaneous damage to the cranial nerves and neurons of the spinal cord.
Having become acquainted with the characteristics of diseases and learning about how encephalitis manifests itself after a tick bite, you must promptly consult a doctor for qualified help.
Treatment and prevention
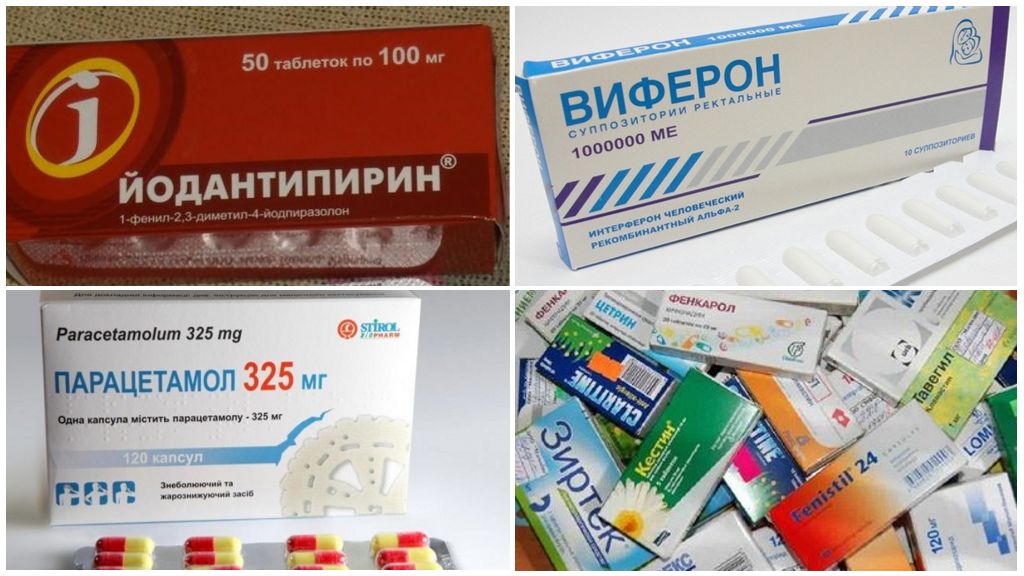
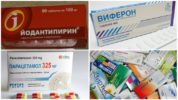
Timely diagnosis of the disease is the basis of a correctly diagnosed and positive prognosis for treatment. Diagnose a virus it is possible by a serological method. It allows you to detect antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis in the patient’s blood and cerebrospinal fluid. The presence of infection can be detected in the tick itself, if subjected to laboratory tests. If a virus is detected in a parasite, a medicine is administered to a person - a specific tick-borne immunoglobulin or appointment is scheduled iodantipyrine.
The treatment of tick-borne encephalitis is complicated by the lack of medications that can have a direct effect on the pathogen. Modern medicine does not have specific drugs that can kill a dangerous virus. Therefore, quite often, patients are interested in the question of whether tick-borne encephalitis is treated.
All therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving symptoms and maintaining the body. It is possible to cure the disease with the help of such dosage forms:
- antiviral drugs - Viferon, Roferon, Cycloferon, Amiksin;
- antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, detoxification, dehydration, anti-shock, antiviral agents, as well as drugs that affect blood microcirculation;
- in the acute phase of tick-borne encephalitis, B vitamins and antihistamines are used.
Clinical recommendations for tick-borne encephalitis prevention allow you to protect the patient from the development of a dangerous ailment. Distinguish:
- Emergency prophylaxis, which is carried out after contact with an encephalitis tick. In this case, the patient is given immunoglobulin in a standard dosage, and after 10 days the vaccination is repeated, but the amount of the drug is doubled.
- Planned specific anti-encephalitis prophylaxis of tick-borne encephalitis. For vaccinations use special vaccines. They are used twice with repeated revaccination.
Tick-borne encephalitis vaccinations It is recommended that one month before the spring season the ticks wake up, but vaccination does not protect for a long time.