- Melon fly
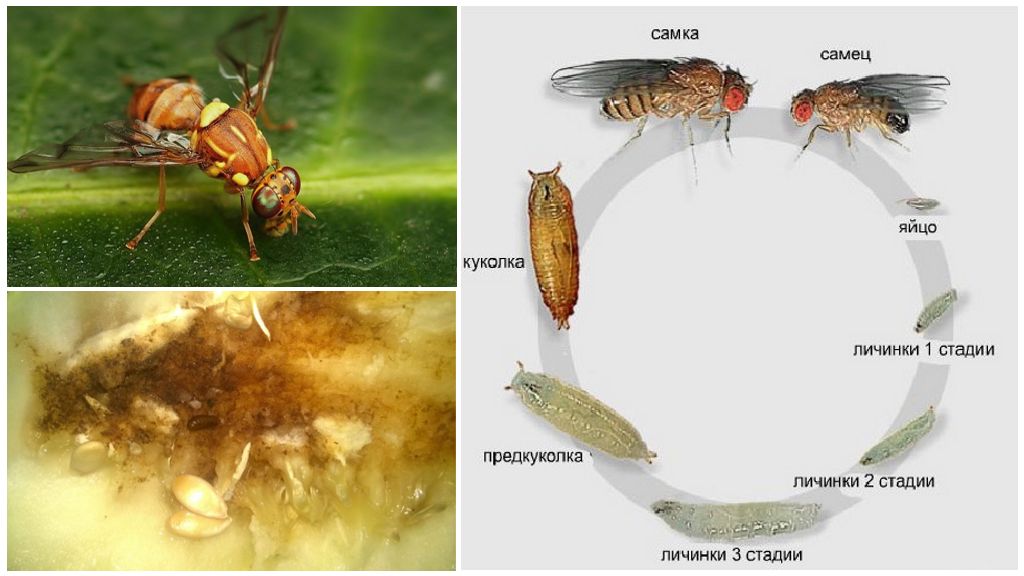
- Melon Fly Development Cycle
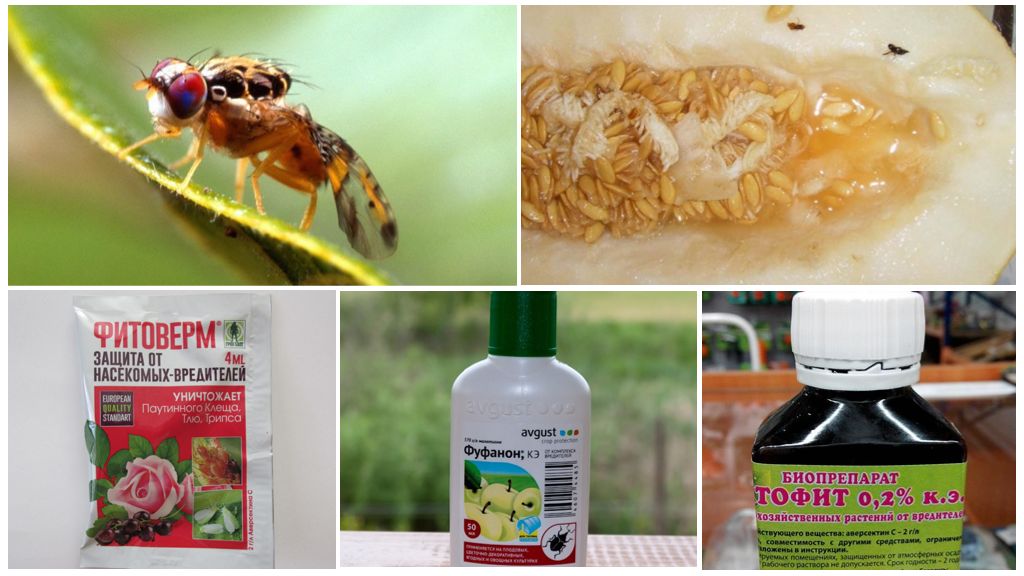
- Chemicals for melon fly control
Melon fly is a dangerous pest of gourds. In Latin it sounds like bactrocera cucurbitae coquillett. Larvae live and feed in pumpkin fruits, adults drink the juices of the same plants. Damage melon, watermelon, cucumbers, pumpkin, wild cucumbers. During the year, under favorable conditions, 3 generations of melon flies appear, puparia winter in the pupal stage.
Description of appearance
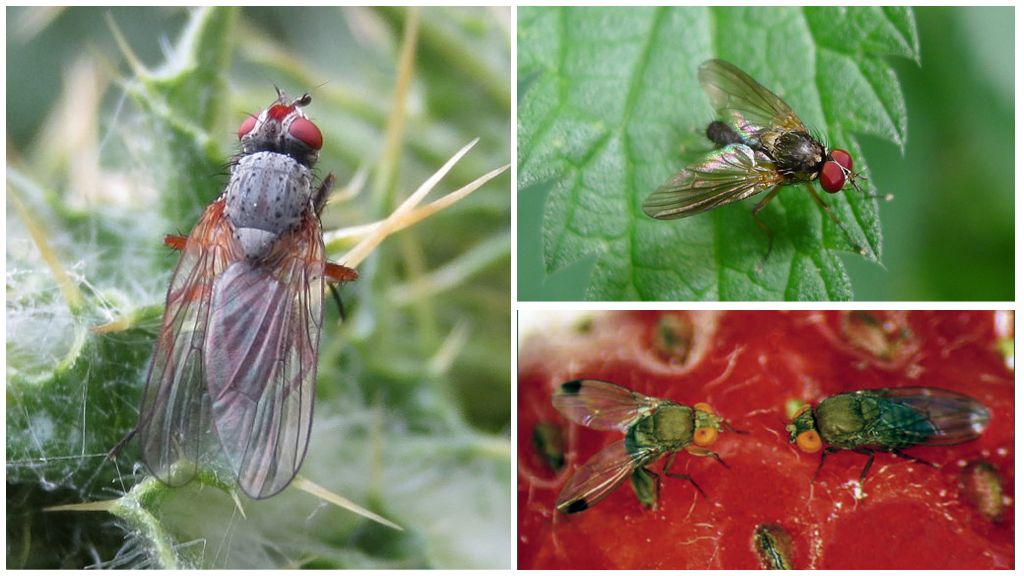
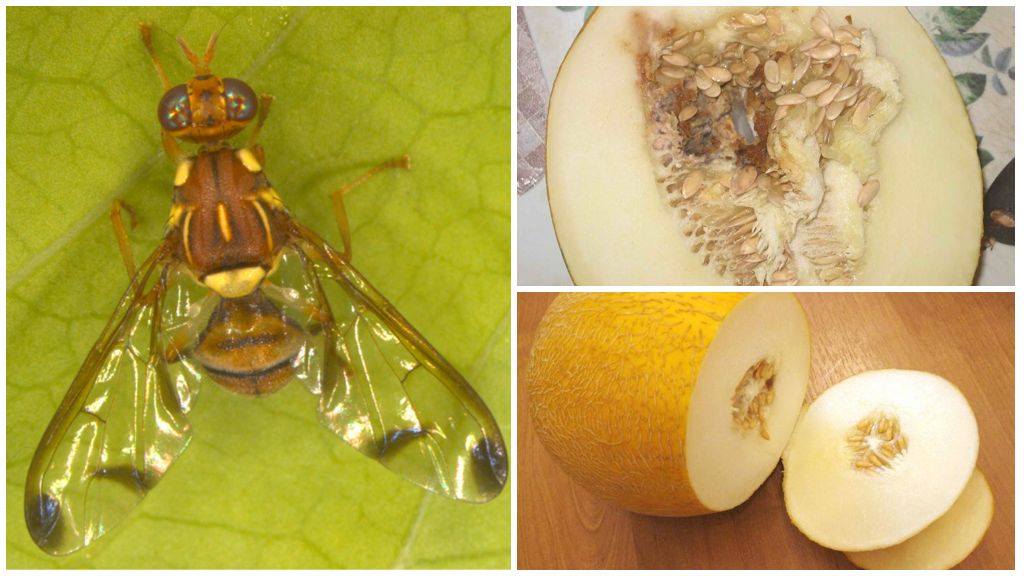
Flies of medium size up to 7 mm, yellow color. Wingspan reaches 5 mm. The head is colored more intensely. The whole body is covered with small thick hairs. A pair of transparent wings with four transverse yellow stripes. There are small antennae on the head, well-defined eyes. A photo of a melon fly can be seen below.
The larva is born extremely small - about 1 mm. As it grows, it grows to 11 mm. The body is cylindrical dirty yellow, expands to the rear end, smooth. At the last stage of development pupation occurs.
On a note!
Pupa is dark yellow, closer to brown. Size - 8 mm. In this state, the melon fly hibernates. With the development of larvae in early summer, in a few days an adult appears. The ability to fertilize develops during the day.

Life cycle
The spring years coincide with the formation of fruits in the spring. By that time, the soil temperature is warming up to +20 degrees Celsius. The summer period stretches in time up to 30 days. Over the entire warm season, about 3 generations succeed. Melon flies parasitize from early June to October.
The life expectancy of adult females is 2 months, males die after the end of summer. Female eggs are laid almost every day in the forming fruits, one in each. Avoids large fruits where the skin becomes dense. Deepens eggs under the skin by 2 mm.
On a note!
On the throughout life the female lays 100 eggs.
The female eats juices of the same cultures. The droplets protrude to the surface, calmly pulling them in with a long proboscis. The males do not damage the fruit on their own, but use the holes that the females made.
Larval development A melon fly in an egg lasts from 2 days to a week, depending on climatic conditions. After exiting the shell, the worm penetrates deep into the fetus. It feeds on seeds, juice, pulp. Sheds 3 times. The whole development cycle in the summer lasts 8-13 days, in the autumn it lasts up to 18 days. After the third molt, they leave the fruit, burrow into the ground. On clay soils, it makes its way deep into 13 cm.
The development of the pupa lasts about 20 days. Autumn puparia winter. In early summer, when the soil warms up to +20 degrees Celsius, adults appear. A few days later, years begin.
Harm done
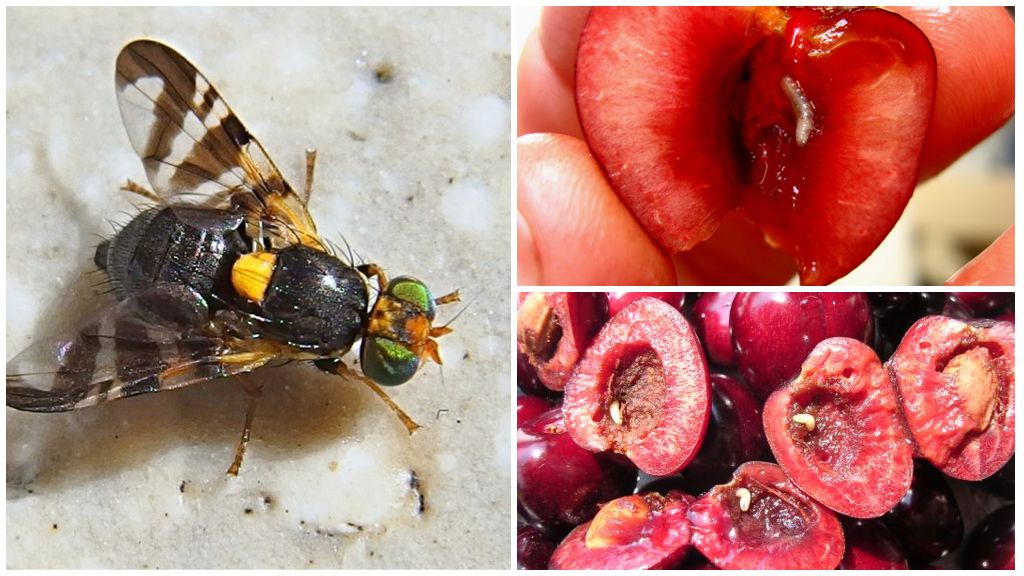
The main pests are melon fly larvae. Damage the fetus from the inside, making it unfit for consumption, slow down the formation, reduce the quality, quantity of the crop. Adult flies are harmful by piercing the skin. Pathogens penetrate into the lesion, bacteria, the process of decay begins
Signs of damage are dark tubercles on the surface of the fetus, holes in the places where the larvae emerge. When cutting, breaking on the pulp, numerous strokes are visible.The affected fruit will rot from the inside; it may look healthy in appearance.
On a note!
The melon fly does not constitute a danger to humans. In case of accidental swallowing of eggs or a small larva, they die in the digestive tract under the influence of enzymes, gastric juice. The imago does not tolerate dangerous diseases. All melon fly control methods relate to crop protection.
Effective Fighting Methods
The insect is common in countries where melons are actively grown. In Russia, lives in the Rostov region, Volgograd, Astrakhan, and the North Caucasus. Actively fighting the parasite in India, Africa, Syria, Turkey, Iraq, Iran. To prevent infection of other territories, products undergo thorough sanitary control, pre-treatment.
Agrotechnical methods of control include deep plowing, crop rotation, the cultivation of early varieties, hybrids. Chemical methods of destruction include treating seeds with pesticides before planting, spraying with chemicals after the first leaves. When using insecticides, it is forbidden to spray crops at the flowering phase, less than 20 days before harvesting.

In Transcaucasia, an ancient method is used to combat the melon fly. After the fruit reaches the size of a chicken egg, it is buried in the soil, where it remains until it ripens.
Flies in a melon can spoil from 70% of the crop per season to 100%. With the threat of mass destruction of melons and gourds, a unique method of pest control was used on Rota Island - they released pre-sterilized males into nature. Further processing of the melon from the melon fly was not required, since the eggs did not form or the larvae did not hatch from them.
Interesting!
African melon fly lives in areas with a hot climate - Africa, America, Asia, Oceania. Motley flies about 8 mm in size. It damages about 125 types of crops, including melon, watermelon, pumpkin, cucumbers, papaya, mango, citrus. To extract the larva from the fetus, immerse it for 4 hours in water, maggot floats to the surface. For catching adults use traps.
Effective drugs
To combat melon fly, biological and chemical preparations are used. They allow get rid of flies as soon as possible.
Biological products do not pose a danger to the environment, eating fruits is allowed after thorough washing under running water. The result is observed within 7-14 days after spraying the crops. Effective remedies Fitoverm, Spark Bio, Mikosan, Actofit, Biospore.
Chemicals act almost immediately. Maximum efficiency is observed in the first 4 hours after treatment, they retain toxic properties for about a month. They are absorbed by the tissues of the culture, they kill the melon fly, larvae during feeding. It is forbidden to apply poison during the flowering period, later than 20 days before harvesting. The concentrate is diluted with cold water immediately before use in the ratio specified in the instructions. Effective remedies - Fufanon, Kemifos, Novaktion, Karate Zion, Agita. The crop should be processed in May, a few weeks before flowering.






